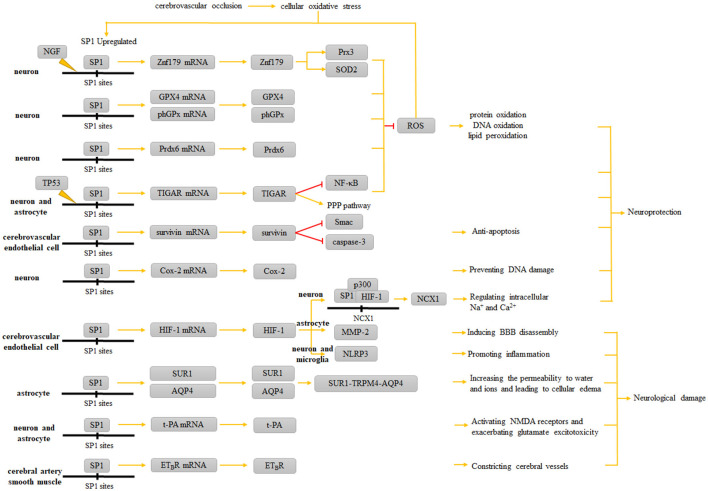
Figure 3.
Role of SP1 in ischemic stroke. When inflammatory responses occur in the corresponding ischemic areas of the brain, increased intracellular SP1 upregulates the expression of Znf179, GPX4, phGPx, Prdx6, and TIGAR, which ultimately resist ROS and ameliorate protein oxidation, structural DNA oxidation and lipid peroxidation; upregulated survivin resists apoptosis; Cox-2 prevents DNA damage; HIF-1 can cooperate with SP1 to form the SP1-p300-HIF-1 complex, which upregulates NCX1 and protects neurons. However, the neurological damage caused by SP1 is reflected in MMP-2 and NLRP3 synthesis induced by the upregulation of HIF-1; upregulated SUR1 and AQP4 exacerbate brain edema; t-PA exacerbates glutamate excitotoxicity; ETBR enables the vasoconstrictive effect of ET-1.