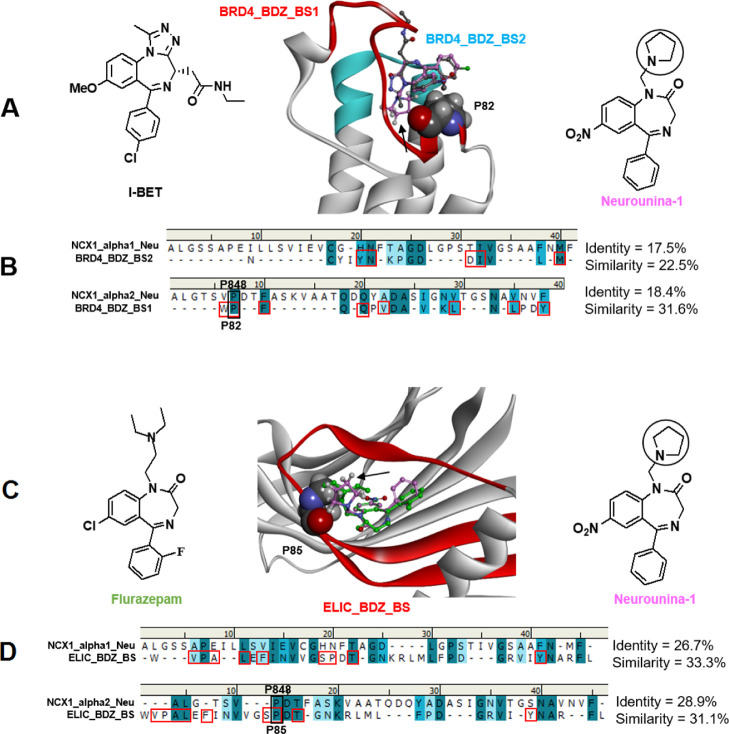
Figure 9.
(A) Calculated Neurounina-1 lowest energy conformation (carbons: pink) superimposed on the X-ray structure of I-BET (carbons: dark gray) in complex with the BRD4 bromodomain (PDB ID: 3P5O). The I-BET binding site is colored in red (BRD4_BDZ_BS_1) and cyan (BRD4_BDZ_BS_2). P85 is evidenced in CPK. The pyrrolidine substituent of Neurounina-1 is indicated by a black arrow. (B) Sequence alignments of the α1 and α2 repeat regions suggested to be involved in Neurounina-1 binding with the BRD4 alprazolam binding site. BRD4 residues establishing interactions with the benzodiazepine ligand are evidenced with red squares. (C) Calculated Neurounina-1 lowest energy conformation (carbons: pink) superimposed on the X-ray structure of flurazepam (carbons: green) in complex with ELIC (PDB ID: 2YOE). The binding site is colored in red (ELIC_BDZ_BS). P82 is evidenced in CPK. The pyrrolidine substituent of Neurounina-1 is indicated by a black arrow. (D) Sequence alignments of the α1 and α2 repeat regions suggested to be involved in Neurounina-1 binding with the ELIC flurazepam binding site. ELIC residues establishing interactions with the benzodiazepine ligand are evidenced with red squares. NCX1 P848, BRD4 P82, and ELIC P85 proline residues are evidenced and labeled.