Fig. 2.
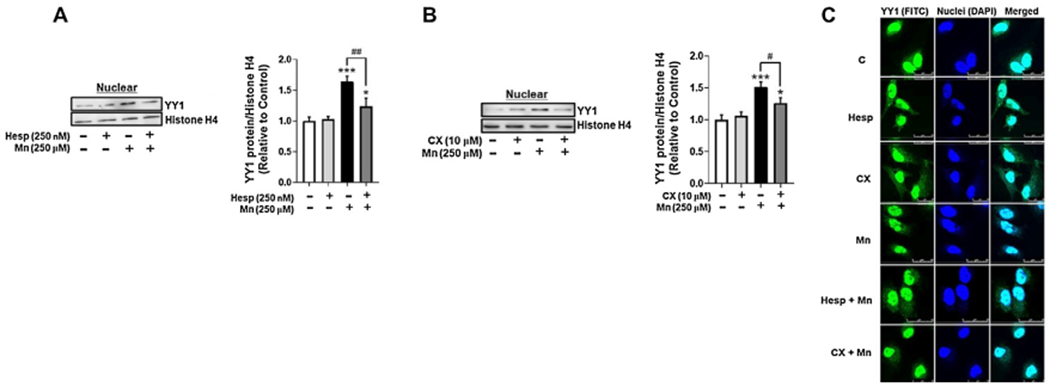
Mn-induced YY1 phosphorylation via AurkB and CK2 leads to YY1 nuclear translocation. (A) Astrocytes were pre-treated with Hesp (250 nM, 1 h) and exposed to Mn (250 μM, 3 h), then cells were fractionated and analyzed for YY1 protein levels in the nuclear fraction by western blotting. Nuclear protein histone H4 was used as a loading control. (B) Astrocytes were pre-treated with CX (10 μM, 1 h) and exposed to Mn (250 μM, 3 h), then cells were fractionated and analyzed for YY1 protein expression in the nuclear fraction by western blotting. (C) Astrocytes were pre-treated with Hesp or CX and exposed to Mn for the indicated time periods, then analyzed via immunocytochemistry (ICC) for YY1 nuclear expression. Scale: 0-25 μM. (*p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, compared to the control; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test; N = 3).
