Fig. 6.
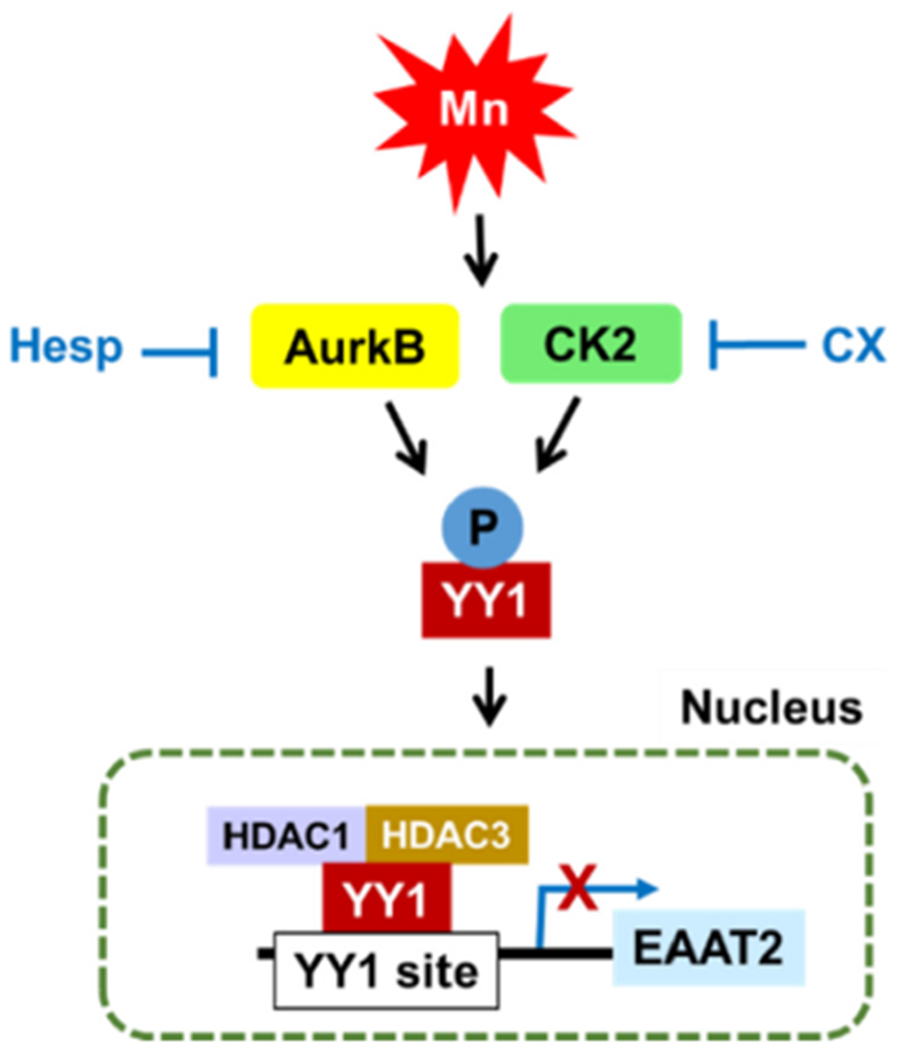
Proposed mechanism of Mn-induced EAAT2 repression via YY1 phosphorylation in astrocytes. Mn induces phosphorylation of YY1 at serine residues via the kinases AurkB and CK2, leading to YY1 nuclear translocation, YY1/HDAC interaction, YY1 binding to the EAAT2 promoter, followed by consequent repression of EAAT2.
