Fig. 7. PTB prevention and behavioral analyses for P4/SAHA treatments.
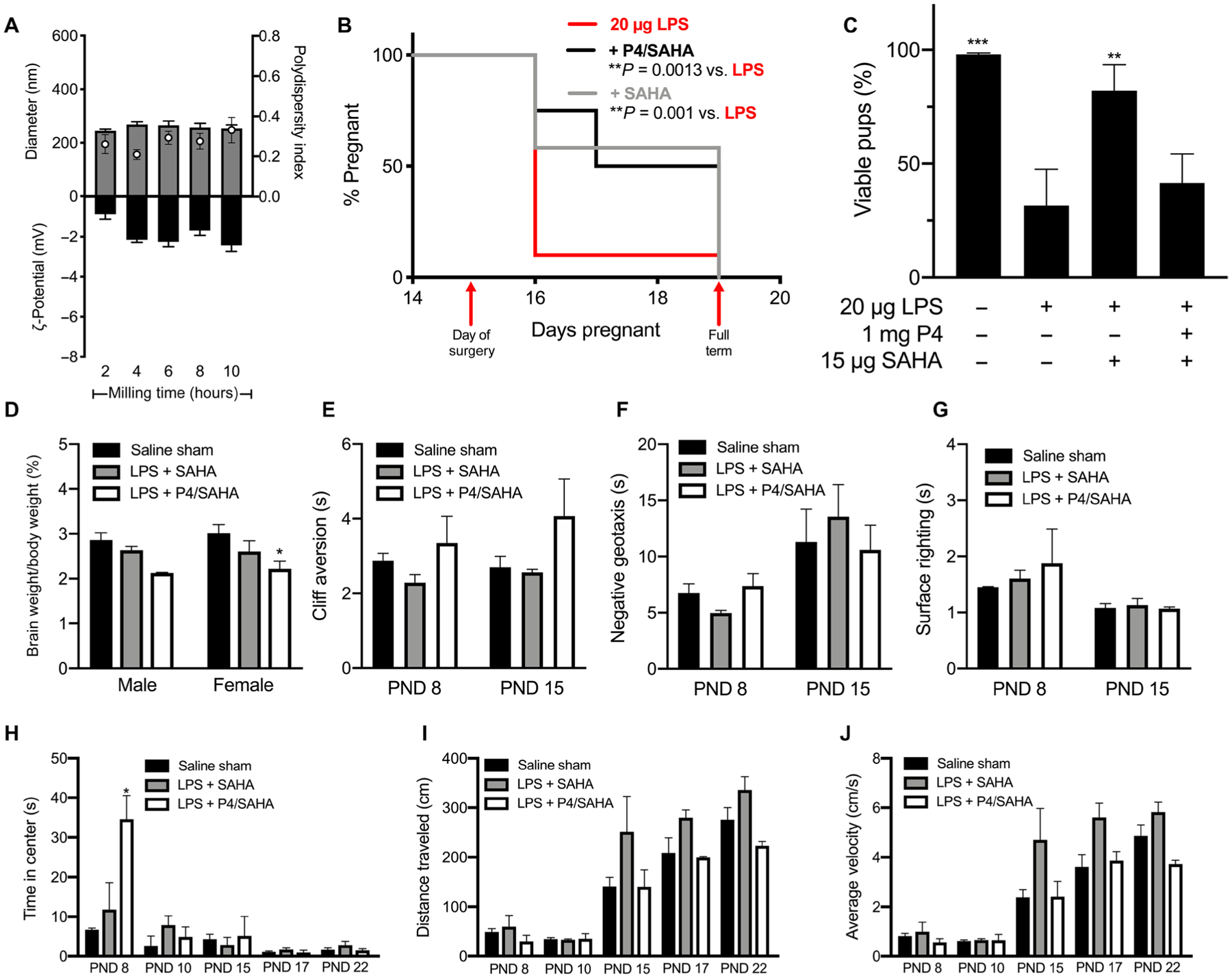
(A) Diameter (gray bars), PDI (white dots), and ζ-potential (black bars) of SAHA NS (1.5 mg/ml) over 10 hours of nanomilling. Data are represented as means ± SEM (n ≥ 3). (B) Pregnancy survival curves showing the percentage of animals remaining pregnant after DDI of 20 μg of LPS on E15. Daily vaginal administration of various doses of SAHA NS (15 μg, n = 12) or P4/SAHA (1 mg/15 μg, n = 12) provided a significant reduction in PTB rates compared to LPS alone (n = 20) (**P < 0.005, Mantel-Cox test). (C) For term litters, the percentage of pups born live compared to viable pups counted on E15. **P < 0.001 and ***P < 0.0001 compared to LPS. Data are presented as means ± SEM (n ≥ 12 litters). (D) Pup brain weight as a percentage of body weight for pups from the saline sham–treated, 20 μg of LPS + SAHA (15 μg), or LPS + P4/SAHA (1 mg/15 μg) group. *P = 0.027. (E to J) Behavioral tests for pups in the saline sham–treated, 20 μg of LPS + SAHA (15 μg), or LPS + P4/SAHA (1 mg/15 μg) group: (E) cliff aversion, (F) negative geotaxis, (G) surface righting, (H) time in center for open field (*P = 0.02), (I) distance traveled in open field, and (J) average velocity in open field. Failures were not included in data analysis. Data are presented as means ± SEM (n ≥ 3 litters).
