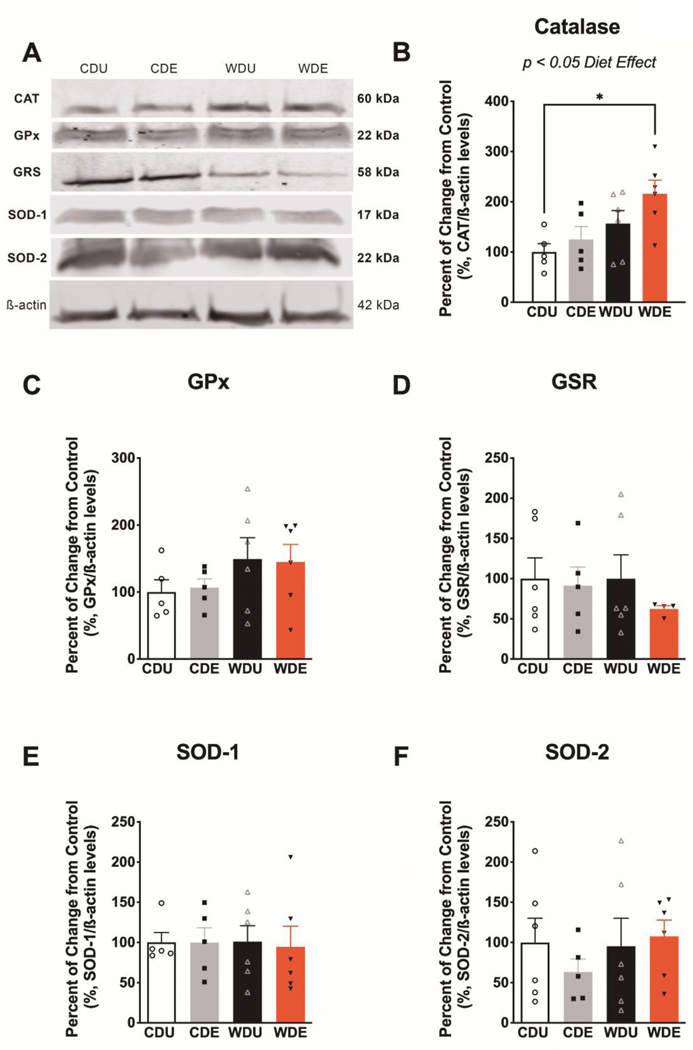
Figure 4. Increased catalase protein levels in the brain of rats exposed to an obesogenic diet.
(A) Representative Western blot bands from whole-brain homogenates illustrating the relative levels of critical proteins involved in the brain antioxidant network. Protein levels are expressed in percent from control and normalized in relation to 𝝱-actin. (B) The obesogenic WD increased catalase protein levels in the brain [diet: F(1,18) = 8.60, p = 0.0090]. This effect was particularly evident in WDE rats relative to CDU (post-hoc p = 0.03), indicating that PS exacerbates the effect of an obesogenic diet on catalase protein levels. The protein levels of glutathione peroxidase (C), glutathione reductase (D), superoxide dismutase 1 (E), and superoxide dismutase 2 (F) were not significantly affected by the dietary and stress manipulations (for main and interaction effects: p > 0.05). n = 5–6 rats/group. Error bars are S.E.M.