Figure 4. NR enhances aerobic and anaerobic respiration in both mouse and human muscle stem cells.
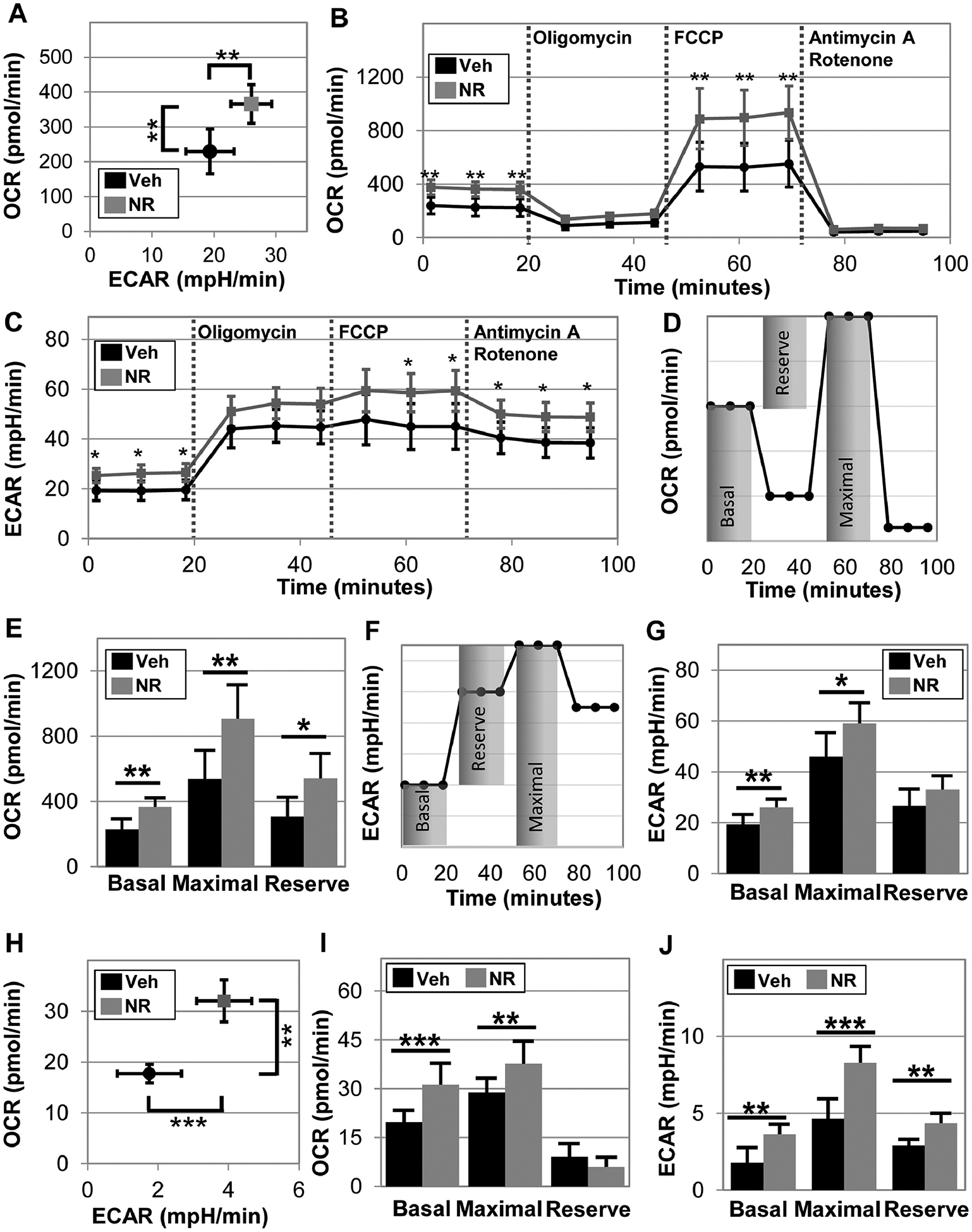
Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) and extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) were measured in mouse derived stem cells using a seahorse extracellular flux analyzer following 24 hours of 0.5 mM NR treatment (A). In the same experiment, Oligomycin, FCCP, Antimycin A and Rotenone were applied in the assay to determine maximal and reserve respiration of the mouse stem cells (B) and maximal and reserve ECAR (C). The schematics for calculation of basal, maximal, and reserve values for OCR (D) and ECAR (E). Next, this methodology was applied to human derived myoblast. OCR vs. ECAR graph suggests that NR treatment shifts human myoblasts toward a more energetic phenotype (H). Basal, maximal, and the reserve (difference between basal and maximal) aerobic (I) and anaerobic (J) respiration were determined following 24 hours of NR treatment. Data represents the mean of 4 to 5 wells per condition, which each experiment performed for three different donors to ensure repeatability. Statistical significance indicated by “*” p < 0.05, “**” p < 0.01, and “***” p < 0.001.
