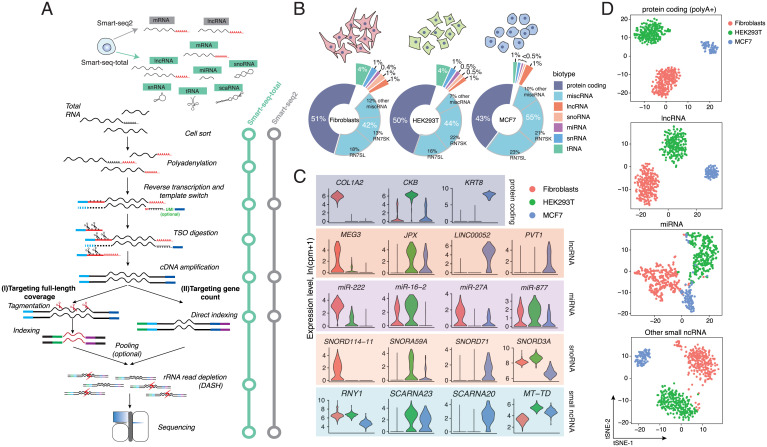
Fig. 1.
Smart-seq-total performance. (A) Schematic comparison of Smart-seq2 and Smart-seq-total pipelines. Following cell lysis, total cellular RNA is polyadenylated, primed with anchored oligodT, and reverse transcribed in a presence of the custom degradable TSO. After reverse transcription, TSO is enzymatically cleaved, single-stranded cDNA is amplified and cleaned up. Amplified cDNA is then either tagmented or directly indexed, pooled, and depleted from ribosomal sequences using DASH (23). The resulting indexed libraries are then pooled and sequenced on Illumina platform. (B) Distribution of mapped reads across RNA types in human primary fibroblasts, HEK293T, and MCF7 cells. Percentage of total reads mapped to each RNA type. miscRNA class is additionally split into RN7SK, RN7SL, and other miscRNA categories. (C) Examples of coding and noncoding marker genes for each cell type. Top exemplary markers per biotype computed among cell types using Wilcoxon rank sum test. RNY1 belongs to miscRNA, SCARNA23 and SCARNA20 to scaRNA, MT-TD to mitochondrial tRNA class. (D) t-SNE plots of three profiled human cell types generated using indicated subset of genes. From top to bottom: protein coding, lncRNA, miRNA, and other small ncRNA (include snoRNA, snRNA, scaRNA, scRNA, and miscRNA). We have excluded histone coding genes from the protein coding (polyA+) set, since a large fraction of these RNAs are known to lack polyA tails (60).