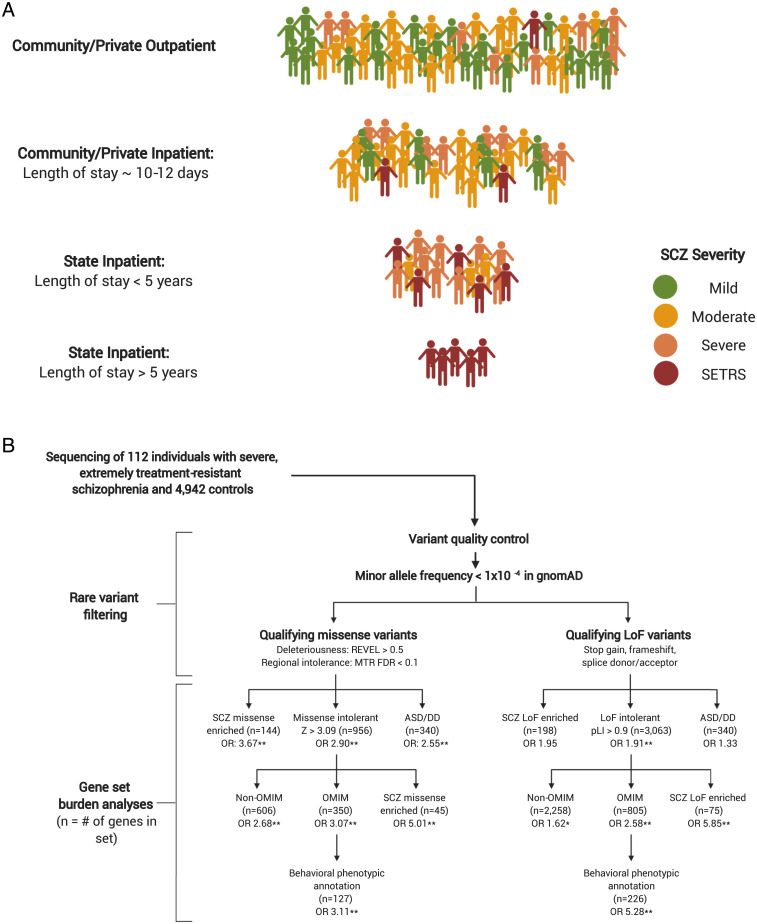
Fig. 1.
Study and analysis workflow. (A) Approximate distribution of illness severity within the schizophrenia spectrum by system of care (numbers not to scale). Typically, patients who do not respond to treatment after several months in community inpatient facilities are transferred to state-funded inpatient facilities and represent a more severe form of schizophrenia. Patients who require very long stays (>5 y) in state-funded inpatient facilities represent the most severe and treatment-resistant subset of the schizophrenia spectrum, which we define as severe, extremely treatment-resistant schizophrenia (SETRS). SCZ: Schizophrenia. (B) Analytic workflow of 112 individuals with SETRS and 4,929 controls. Qualifying missense and loss-of-function variants are analyzed separately in their respective gene sets. SCZ missense enriched: Genes with prior evidence of enrichment for missense variation in the schizophrenia exome meta-analysis (SCHEMA) study of schizophrenia. SCZ loss-of-function enriched: Genes with prior evidence of enrichment for loss-of-function variation in SCHEMA. ASD/DD: combined gene set of 102 genome-wide significant genes associated with autism spectrum disorder and 299 genome-wide significant genes associated with developmental delay. OMIM: All genes associated with Mendelian disorders in the OMIM database. Non-OMIM: Missense and loss-of-function intolerant genes without a known disease association in OMIM. Behavioral OMIM: The subset of OMIM genes with clinical phenotype annotations including “behavioral” manifestations. *P < 0.05; **FDR < 0.1.