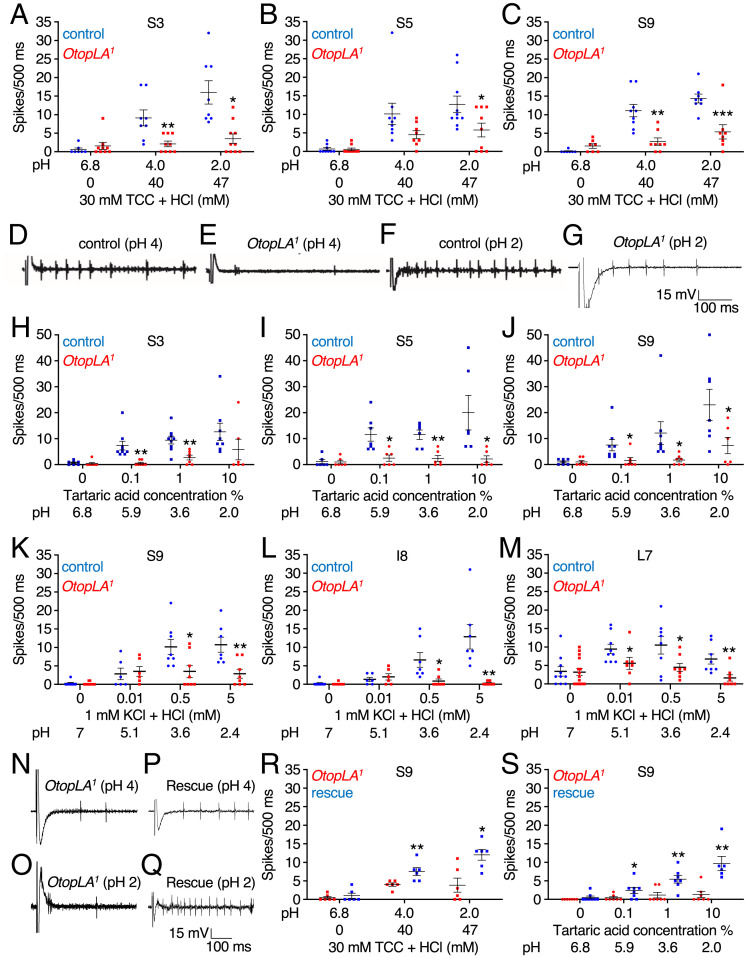
Fig. 3.
Tip recordings showing that mutation of OtopLA impairs acid-induced action potentials. (A–C) Tip recordings from the indicated S-b class sensilla (22) due to stimulation with HCl at the indicated pH values. Shown are the mean action potentials during the first 500 ms of the recordings with the control (w1118) and OtopLA1. The pH 6.8 solution contained only the electrolyte (30 mM TCC). (A) Responses of S3 sensilla to HCl. Control, n = 7 to 8. OtopLA1, n = 9 to 10. (B) Responses of S5 sensilla to HCl. Control, n = 9 to 10. OtopLA1, n = 8 to 19. (C) Responses of S9 sensilla to HCl. Control, n = 7 to 9. OtopLA1, n = 7 to 8. (D–G) Representative traces for the first 500 ms obtained from S9 sensilla from control (w1118) and OtopLA1 flies during exposure to HCl at pH 4 or 2. (H–J) Tip recordings from the indicated S-b class sensilla stimulated with tartaric acid at the indicated pH values. Shown are the mean action potentials during the first 500 ms of the recordings with the control (w1118) and OtopLA1. The 0% tartaric acid solution consisted only of the electrolyte (30 mM TCC). (H) Responses of S3 sensilla to tartaric acid. Control, n = 7 to 9. OtopLA1, n = 6 to 7. (I) Responses of S5 sensilla to tartaric acid. Control, n = 6 to 7. OtopLA1, n = 6. (J) Responses of S9 sensilla to tartaric acid. Control, n = 7 to 8. OtopLA1, n = 6 to 7. (K–M) Tip recordings from the indicated class of sensilla due to stimulation with HCl at the indicated concentrations and pH values. Shown are the mean action potentials during the first 500 ms of the recordings with the control (w1118) and OtopLA1. The 0% HCl solution contained only the electrolyte (1 mM KCl). (K) Responses of S9 sensilla to HCl. Control, n = 6 to 8. OtopLA1, n = 8 to 12. (L) Responses of I8 sensilla to HCl. Control, n = 6 to 9. OtopLA1, n = 6 to 13. (M) Responses of L7 sensilla to HCl. Control, n = 8 to 9. OtopLA1, n = 8 to 16. (N–Q) Testing for rescue of the deficit in HCl-induced action potentials in OtopLA1 flies expressing the OtopLAp transgene. Representative traces for the first 500 ms obtained from S9 sensilla of OtopLA1 and OtopLA1;lexAop-OtopLAp (rescue) flies upon stimulation with HCl at pH 4 or 2. In all cases, 30 mM TCC was used as the electrolyte. (R) Assaying for changes in mean HCl-induced action potentials in OtopLA1 flies expressing the OtopLAp transgene (rescue). The mean action potentials were during the first 500 ms from S9 sensilla stimulated with HCl at the indicated pHs. OtopLA1, n = 6 and OtopLA1;lexAop-OtopLA (rescue), n = 6. (S) Assaying for changes in mean tartaric acid-induced action potentials in OtopLA1 flies expressing the OtopLAp transgene (rescue). The mean action potentials were during the first 500 ms from S9 sensilla stimulated with tartaric acid at the indicated pH values. We used 30 mM TCC as the electrolyte. OtopLA1, n = 7 and OtopLA1;lexAop-OtopLA (rescue), n = 6 to 8. Student’s unpaired t tests. Error bars, SEMs. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.