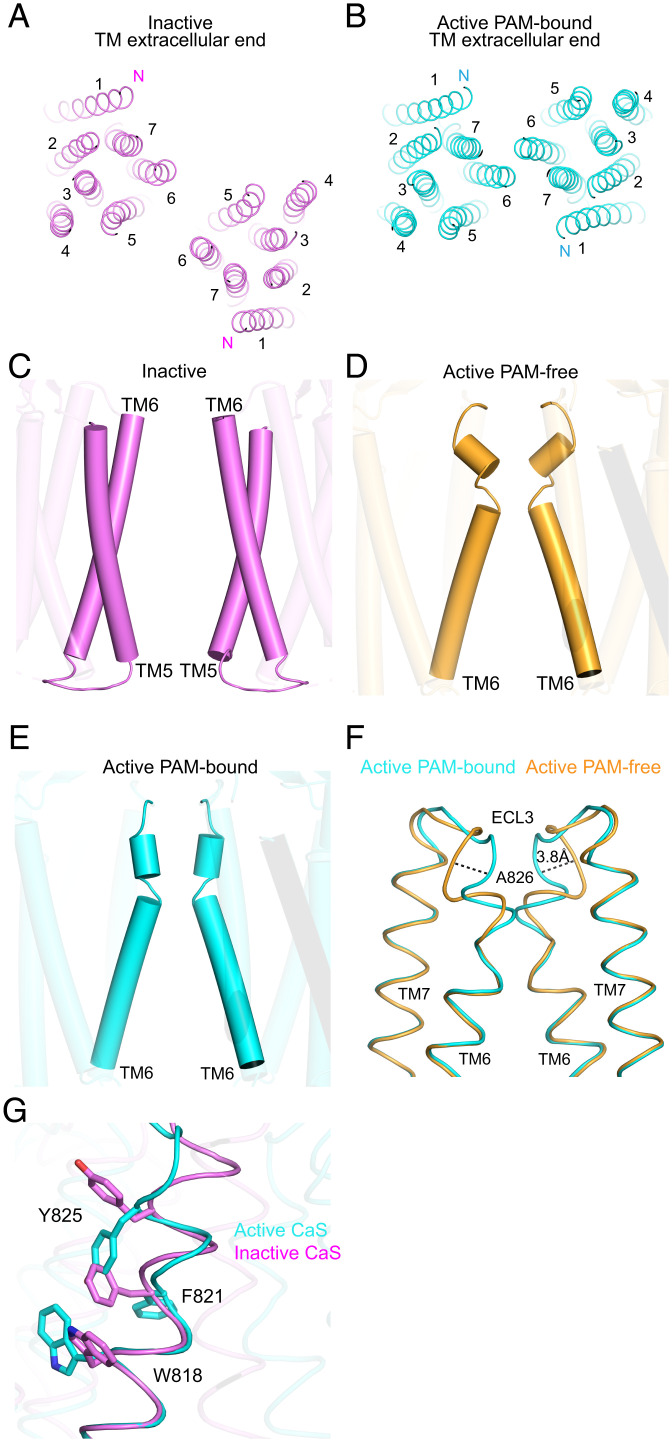
Fig. 2.
Activation-induced conformational changes in the TM. (A and B) TM dimer structures of the NAM-bound inactive (A) and PAM-bound active (B) CaS receptors viewed from the extracellular end. (C–E) Structural elements at the homodimer interface of the NAM-bound inactive (C), PAM-free active (D), and PAM-bound active (E) CaS receptors viewed from the side. (F and G) Alignment of the TM6 helix and ensuing ECL3 region based on residues in the intracellular portion of the TM6 helix (A8046.36 to I8166.48). The diagrams show the comparison between PAM-bound and PAM-free active forms (F) as well as that between the PAM-bound active and NAM-bound inactive states (G).