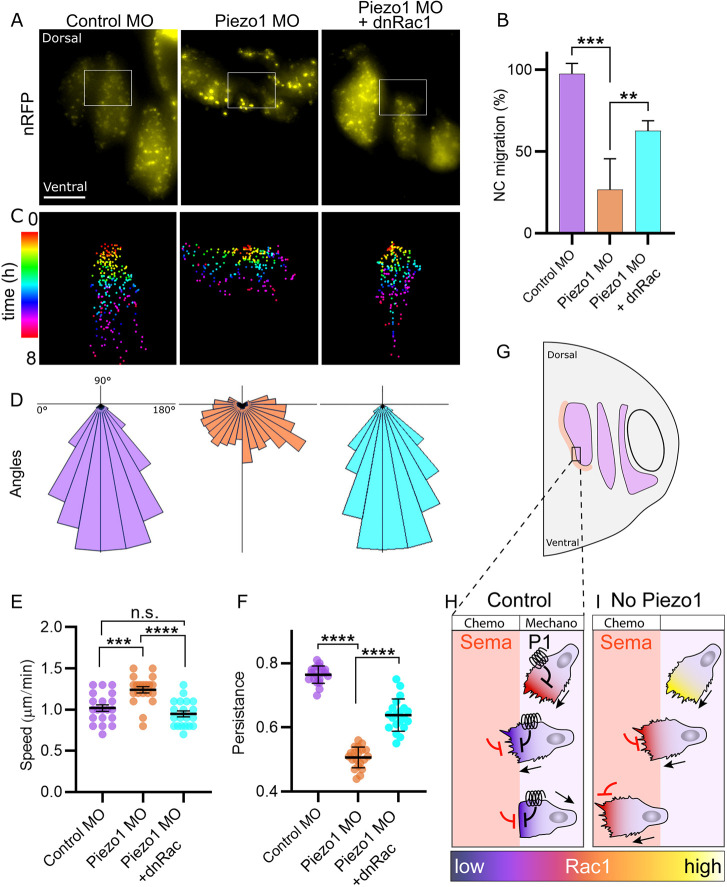
Fig. 7.
Piezo1 prevents neural crest invasion via Rac1 inhibition. (A) NC graft of control (left), Piezo1 MO (middle) and Piezo1 MO plus dominant negative (dn) Rac1 (right). (B) Quantification of the percentage of embryos with normal NC migration from A. Normal NC migration of grafting experiments was determined by comparing the NC migratory streams to a whole-mount in situ hybridization. Note that expression of dnRac1 on top of Piezo1 MO partially rescues NC migration. n=5 embryos per condition. (C) Colour coded single cell tracks from boxed areas in A. Note that Piezo1 MO cells migrate laterally, whereas directional migration is restored in Piezo1 MO plus dnRac1. (D) Angles of cell migration from C. (E) Quantification of speed of cell migration from A. (F) Quantification of persistence of cell migration from A. Note that both speed and persistence of cell migration are rescued in Piezo1 MO plus dnRac1. n=20 in each condition (E,F). Error bars are ±s.e.m. Each dot is the mean value of an independent experiment. All data are representative of at least three biological replicates. **P≤0.01, ***P≤0.001, ****P≤0.0001 (one-way ANOVA with a Dunnett's multiple comparisons post-test). n.s., non-significant. (G-I) Proposed model of the role of Piezo1 (P1) in NC migration. In control embryos (H) Piezo1 mechanical activation partially reduces Rac1 activity, which is further inhibited by chemical signals from Sema. This leads to a collapse of cell protrusions and inhibition of cell migration into the Sema region. In the absence of Piezo1 (I), there is no initial regulation of Rac1 levels: when NC cells reach the Sema region, Rac1 levels are only partially inhibited, and cells continue to invade the Sema region. Scale bar: 100 µm.