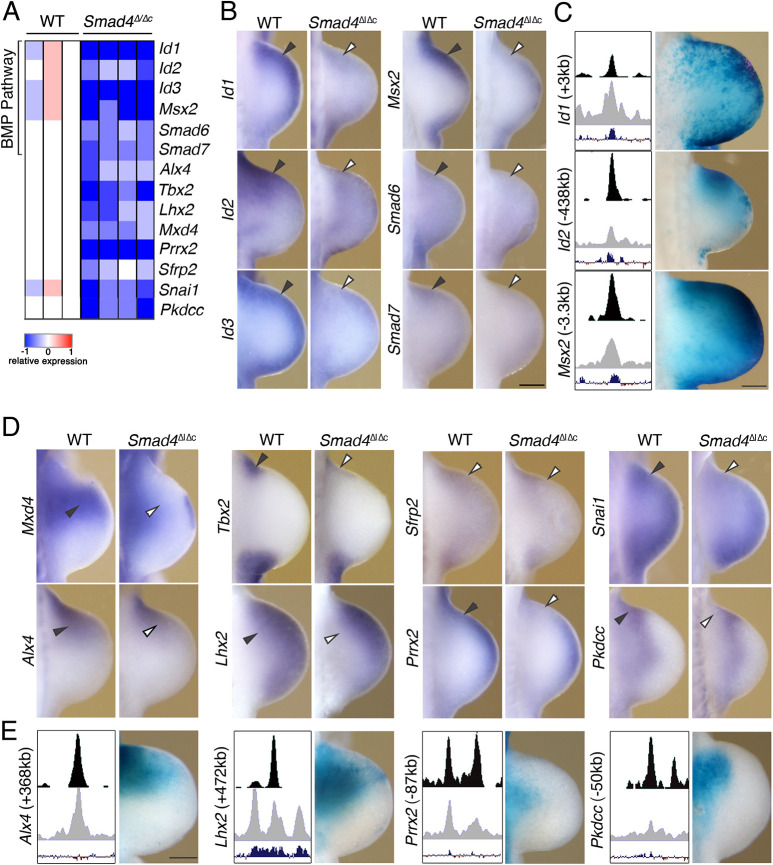
Fig. 6.
Target genes positively regulated by SMAD4 in the anterior forelimb bud mesenchyme. (A) Heat map of the target genes, the expression of which is positively regulated by SMAD4 in the anterior forelimb bud mesenchyme. For each gene, the log2-ratio between the expression level in each sample and the mean of the three biological replicates for wild-type (WT) forelimb buds is shown. Red indicates increased expression and blue indicates reduced expression in comparison with the mean of the wild-type samples. (B,D) Comparative whole-mount in situ hybridization analysis of selected BMP pathway genes (B) and SMAD4 target genes (D) whose spatial expression in the anterior limb bud mesenchyme is altered in Smad4Δ/Δc forelimbs at E10.0 (28-31 somites). (C,E) Analysis of the LacZ reporter activity of SMAD4-enriched candidate CRMs associated with selected target genes. Left panels show a scheme depicting the genomic region harboring the CRM with the SMAD4 ChIP-seq peak (top), the ATAC-seq peak (middle) and the evolutionary conservation (bottom). Right panels show the LacZ reporter activity of SMAD4-enriched candidate CRMs in independent transgenic founders embryos with forelimb bud mesenchymal expression at E10.5 for Id1 (n=4), Id2 (n=6), Msx2 (n=5), Alx4 (n=3), Lhx2 (n=2), Prrx2 (n=3) and Pkdcc (n=4). For whole-mount in situ hybridization, n=3 biological replicates from three independent experiments were analyzed per gene and genotype. Scale bars: 250 µm.