Figure 2.
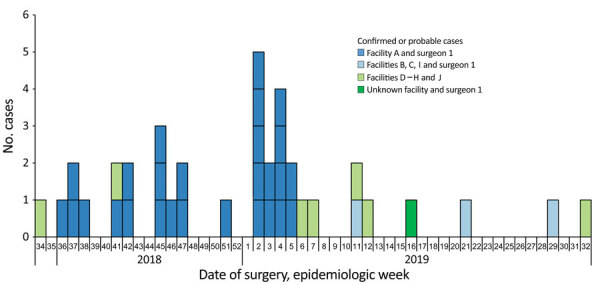
Confirmed and probable cases of infection with Verona integron‒encoded, metallo-β-lactamase‒producing, carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, by week of surgery, among US medical tourists undergoing elective invasive procedures in Tijuana, Mexico, January 2018‒December 2019. Dark blue bars show cases associated with surgery performed at facility A by surgeon 1; light green bars show cases associated with surgery at facilities D–H and J by surgeons other than surgeon 1; and light blue bars show cases associated with facilities B, C, and I by surgeon 1; and dark green bar shows a case associated with surgeon 1 and an unknown facility. A confirmed case was isolation of Verona integron‒encoded, metallo-β-lactamase‒producing, carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa from a patient who had an elective invasive medical procedure in Mexico during January 2018–December 2019 and within 45 days before specimen collection. A probable case was isolation of carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa, with an isolate unavailable for carbapenemase testing, from a patient who had an elective invasive medical procedure in Mexico during January 2018–December 2019 and within 45-days before specimen collection. No cases were identified from patients who underwent surgery before August 2018 (week 34). The peak of the outbreak encompassed epidemiologic weeks 2–5 (January 2019).
