Figure 7.
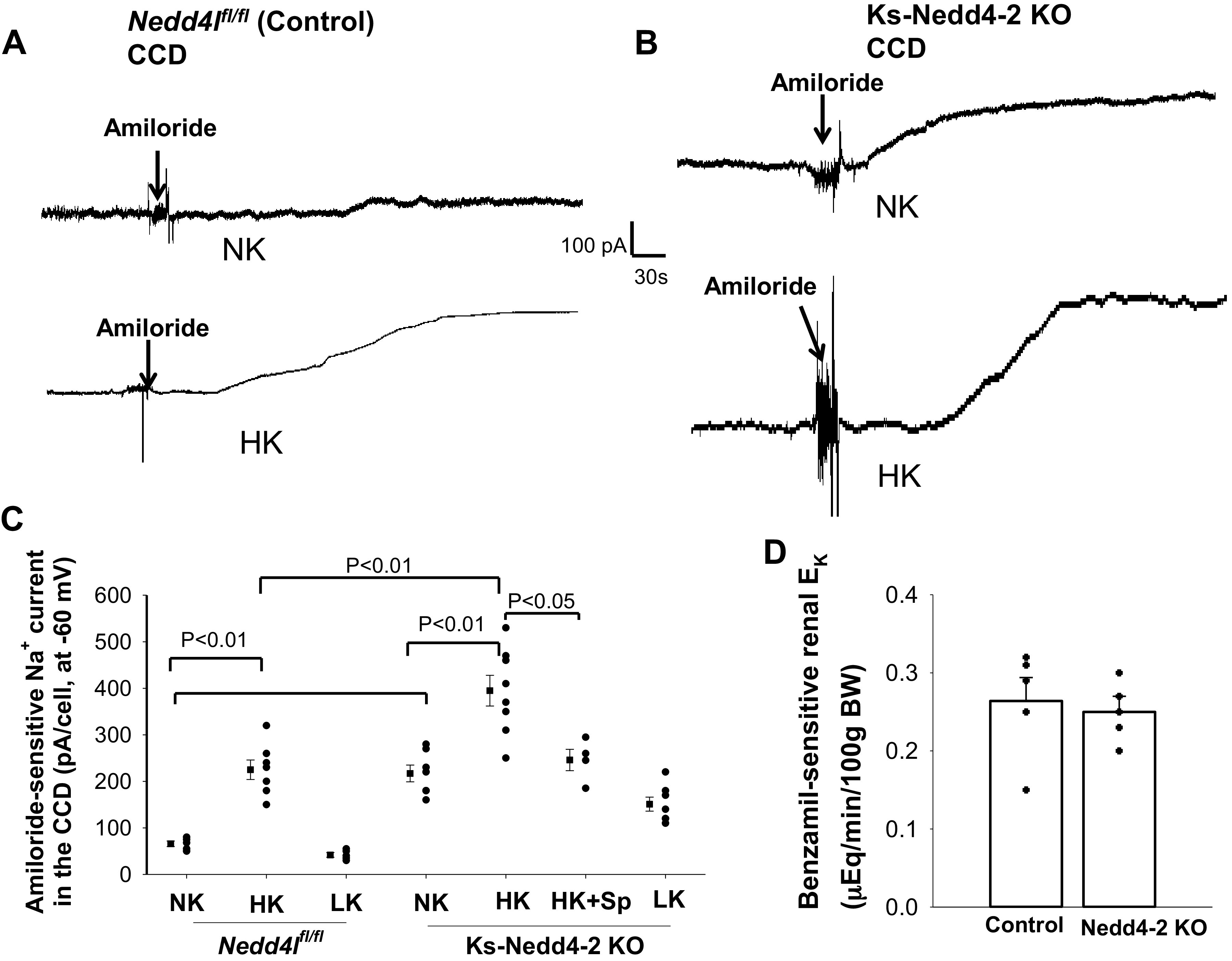
Deletion of neural precursor cell-expressed developmentally downregulated protein 4-2 (Nedd4-2) enhanced high K+ (HK)-induced stimulation of the epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) in the cortical collecting duct (CCD). A and B: sets of gap-free recordings showing amiloride-sensitive Na+ currents in the CCD measured at −60 mV with the perforated whole cell patch in male control mice (A) and in male kidney-specific neural precursor cell-expressed developmentally downregulated protein 4-2 knockout (Ks-Nedd4-2 KO) mice (B) on normal K+ (NK) and HK (7 days). C: scatterplot summarizing the results of experiments in which amiloride (10 µM)-sensitive Na+ currents were measured at −60 mV in male control mice (n = 5–7 tubules), in male Ks-Nedd4-2 KO mice on different K+ diets for 7 days (n = 5–8 tubules), and in male Ks-Nedd4-2 KO mice on HK plus spironolactone (Sp) for 7 days (n = 4 tubules). Mean values and SEs are shown on the left of each column. An arrow indicates the addition of amiloride (10 µM). Significance was determined by two-way ANOVA. Spironolactone was dissolved in ethanol and further diluted at a 1:200 ratio into drinking water. By measuring the volume of water intake, the daily dose of spironolactone for each mouse was 40 mg/kg body wt. D: bar graph (mean value) and scatterplot (each data point) summarizing benzamil (5 mg/1 kg body wt)-induced renal K+ excretion (EK) in male control and Ks-Nedd4-2 KO mice on NK (n = 5 mice). Nedd4l, neural precursor cell-expressed developmentally downregulated 4-like.
