Figure 2.
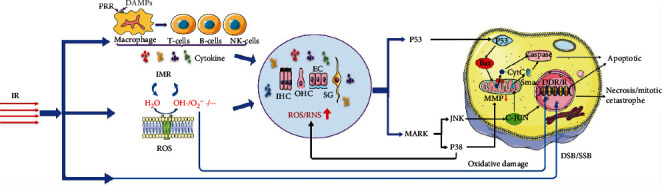
Mechanisms of cell damage induced by ionizing radiation (IR). Radiation can either damage DNA directly or cause oxidative damage to DNA through oxygen free radicals produced by ionizing water molecules, leading to cell death. Damage-associated molecular pattern molecules (DAMPs) will be released after cell damage or death, which activates macrophages and other antigen-presenting cells and enhances inflammatory and immune responses (IMR). Moreover, IMR and reactive oxygen species (ROS) can interact to change the cochlea microenvironment and induce cell death through p53 and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways. DDR/R: DNA damage response and repair reactions pathway; EC: endothelial cells; IHC: inner hair cells; OHC: outer hair cells; SG: spiral ganglion; MMP: mitochondrial membrane potential; DSB: double-strand breaks; SSB: single-strand breaks.
