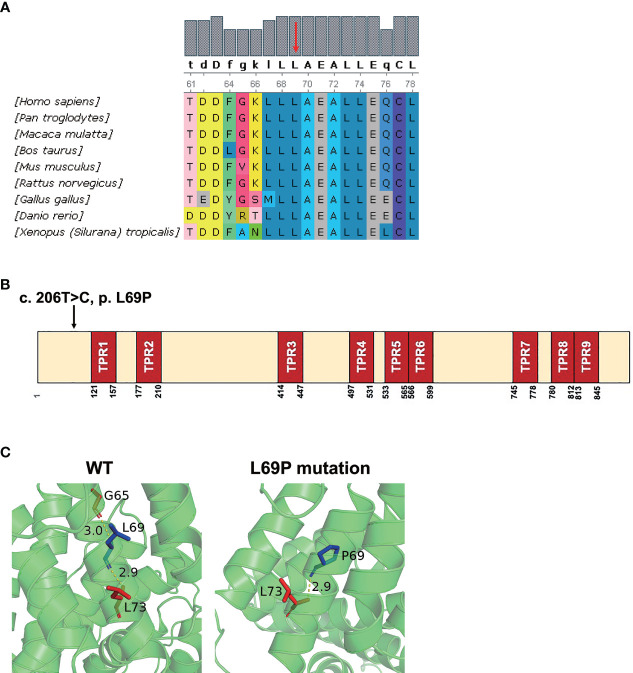
Figure 2.
In silico analysis of the mutant TTC7A and amino acid conservation of p. L69P. (A) Protein alignment indicated that p. L69P amino acids were highly conserved across different species. Residue L69 is shown in red arrow. (B) The schematic structure of TTC7A shows the location of the variant identified in this study. Illustration of TTC7A protein with TPR domains in red and the identified mutation is highlighted by an arrow. (C) The hydrogen bond presenting between Gly65 and Leu69 in the wild-type TTC7A is disrupted by the L69P mutation. The residue 69 together with certain nearby residues within 3Å is illustrated in the wild-type and the mutant by PyMOL. Computed hydrogen bonds are shown as yellow dashed lines. Residues Leu69/Pro69 are highlighted in blue.