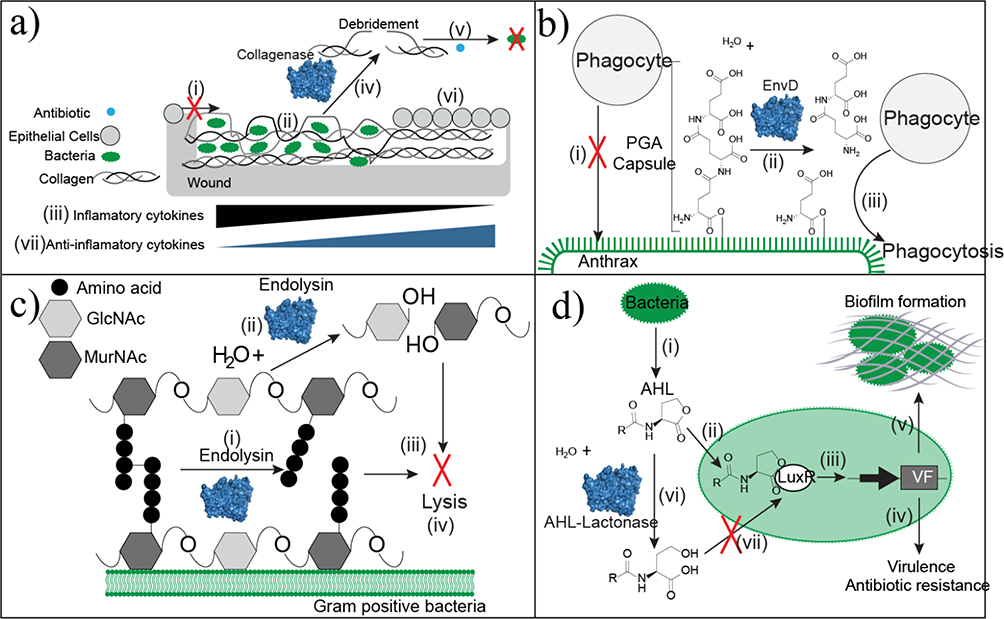
Figure 5.
Approaches of antibacterial enzyme therapeutics. (a) Wound beds that have excessive denatured collagen prevent epithelial cell migration (i) because of the unstable scaffold. Bacteria colonize within the denatured collagen (ii). Infected tissue accumulates the inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β. (iii). Debridement with collagenase specifically cleaves collagen at the sites of denaturation to remove necrotic and unsuitable tissue (iv). Debridement decreases bacterial loads and improves antibiotic penetration as an adjuvant (v). Collagen in its native conformation serves as a healthy scaffold for re-epithelialization. This tissue remodeling is associated with an increase in anti-inflammatory cytokines. (b) Anthrax is protected from phagocytosis by the poly-glutamic acid (PGA) capsule (i). EnvD depolymerizes the protective PGA capsule (ii) leaving anthrax susceptible to phagocytosis (iii). (c) Endolysin strips the peptidoglycan cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria through two mechanisms of action. It hydrolyzes either the peptide cross-linkages within the cell wall (i) or the glycosidic linkage between N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc). Continued depolymerization strips the capsule (iii), which causes bacterial lysis (iv). (d) Bacteria produce the quorum-sensing molecule N-acyl-L homoserine lactone (AHL) (i). AHL binds to the transcription factor LuxR (ii) to activate transcription of genes controlled by the Lux operon (iii). These genes are linked to virulence factors, antibiotic resistance genes (iv), and biofilm formation (v), which limits antibiotic penetration. AHL lactonase hydrolyzes the ester bond of the lactone ring (vi). This structural change disrupts LuxR binding (vii) to block transcription of genes linked to pathogenicity.