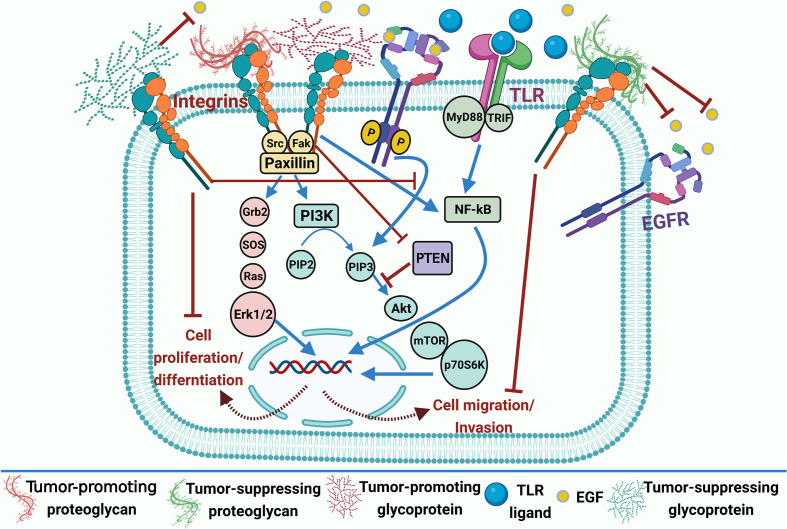
Figure 3.
Dual effect of ECM glycoproteins and proteoglycans in lung cancer. Tumor-promoting glycoproteins (e.g., laminin 5 and fibronectin); laminin expression enhances phospho-EGFR or phospho-Akt expression and loss of PTEN; fibronectin activates toll-like receptors (TLRs) to promote NF-κB activation as well as EGFR-dependent Akt/mTOR/p70S6K signaling pathway; and thus, it stimulates cell proliferation and differentiation in lung cancer. Tumor-promoting proteoglycans (e.g., GPC5) prompted cell migration and metastasis. Tumor-suppressing glycoproteins (e.g., fibulins1,3, and 5) compete with EGF and inhibit EGFR activation. Tumor-suppressing proteoglycans (e.g., GPC3 and SDC‐1) can regulate EGF and many intracellular signaling pathways inhibiting cell invasion and migration. Blue arrows for stimulation; dashed red arrows for cellular effect; and red “T” sign for inhibition.