FIGURE 8.
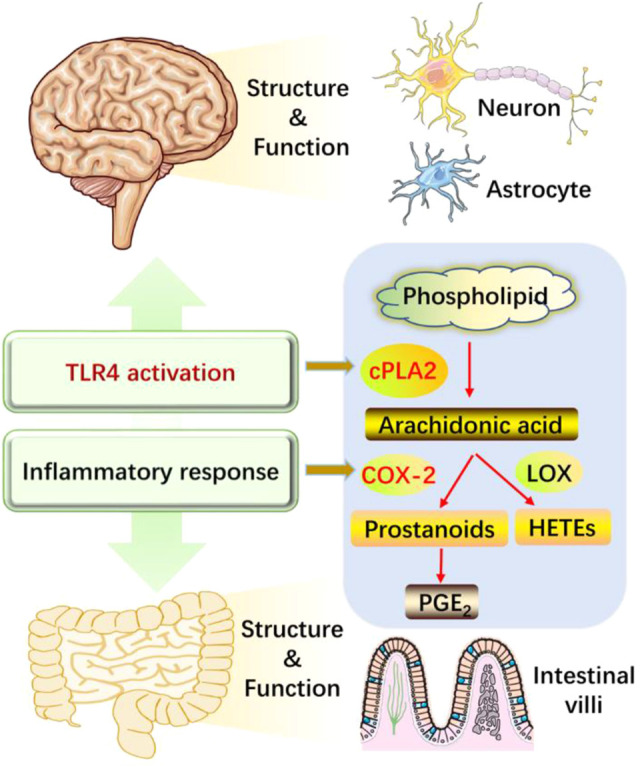
Puerarin protected against HFD/CUMS-induced depression via the TLR4/cPLA2/COX-2 pathway. HFD/CUMS stimulation induced depression-like behavior via increasing inflammatory damages. Inflammatory response is related to TLR4 activation, inducing the changes of structure and function in the brain and small intestine tissues. Puerarin treatment alleviated the depressive phenotype by suppressing TLR4 activation and cytokine over-production, restoring lipid metabolites, inhibiting enzyme activities of cPLA2 and COX-2, and decreasing downstream PGE2 production. HFD: high-fat diet; CUMS: chronic unpredictable mild stress; TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; LOX: lipoxygenase; cPLA2: calcium-dependent cytosolic phospholipases A2; COX-2: cyclooxygenase-2; PGE2: prostaglandin E2; HETEs: hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids.
