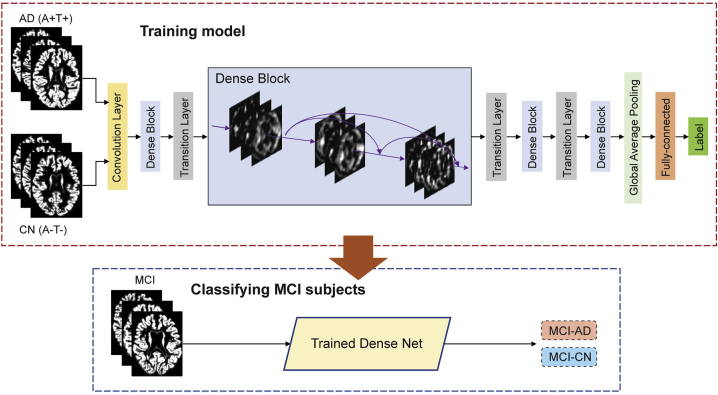
Figure 1.
Study methods
Illustration of proposed deep learning framework. A dense convolutional neural network is trained to differentiate patients with Alzheimer disease (AD) and cognitively normal (CN) controls based on whole-brain GM morphometric data. Subsequently, the trained model is deployed to classify individuals with mild cognitive impairment (MCI), into two groups, MCI-AD and MCI-CN, based on structural morphometric data. AD, Alzheimer’s disease; CN, cognitively normal; MCI, mild cognitive impairment; GM, gray matter.