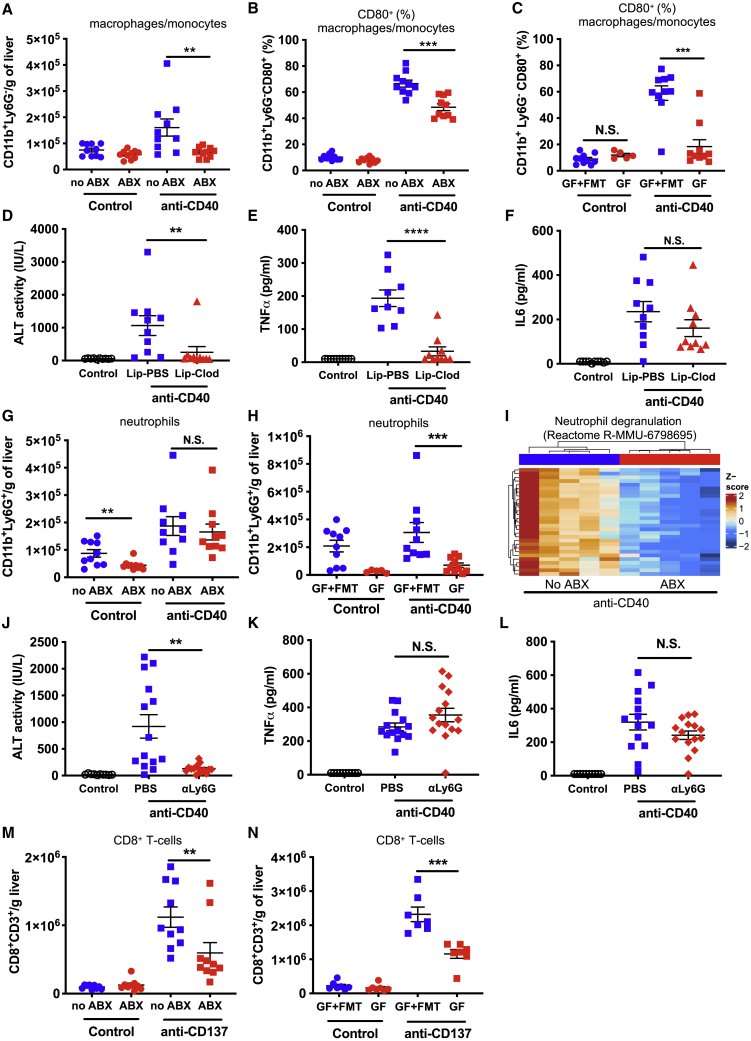
Figure 5.
The gut microbiota modulate anti-CD40- and anti-CD137-induced inflammatory immune cell infiltration and activation in the liver
Flow cytometry analysis was performed on liver cells collected from no ABX and ABX mice or GF and GF mice recolonized by a fecal microbiota transplant (GF+FMT) 24 h after treatment with control (PBS) or anti-CD40 (100 μg i.p.).
(A–C) The number of macrophages/monocytes (CD11b+Ly6G–) per gram of liver (A) and (B and C) the frequency of liver macrophages/monocytes expressing CD80 in (B) no ABX and ABX mice or (C) GF and GF+FMT mice.
(D–F) Levels of (D) ALT, (E) TNFα, and (F) IL6 in serum collected 24 h after control or anti-CD40 treatment of mice that were either treated with control PBS-loaded liposomes (Lip-PBS) or clodronate-loaded liposomes (Lip-Clod) 24 h prior to anti-CD40 treatment.
(G and H) The number of neutrophils per gram of liver in (G) ABX and no ABX or (H) GF and GF+FMT mice.
(I) Heatmap showing the normalized expression of differentially expressed genes in the Reactome neutrophil degranulation pathway. Intensity represents the Z score of log2 library size normalized counts.
(J–L) Levels of (J) ALT, (K) TNFα, and (L) IL6 in serum collected 24 h after control or anti-CD40 treatment of mice that were either treated with PBS or anti-Ly6G (500 μg i.p.) 16 h prior to anti-CD40 treatment.
(M and N) The number of CD8+ T cells in livers collected from (M) ABX and no ABX mice or (N) GF and GF+FMT mice 11 days after treatment initiation with anti-CD137 (100 μg i.p., 3 doses 4 days apart) or PBS. n = 5–10 mice per group.
Statistical significance was determined using a Mann-Whitney test. ∗∗p ≤ 0.01; ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p ≤ 0.0001. N.S., not significant. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Results shown are pooled from two independent experiments (A–H and J–M) or a single experiment (N).