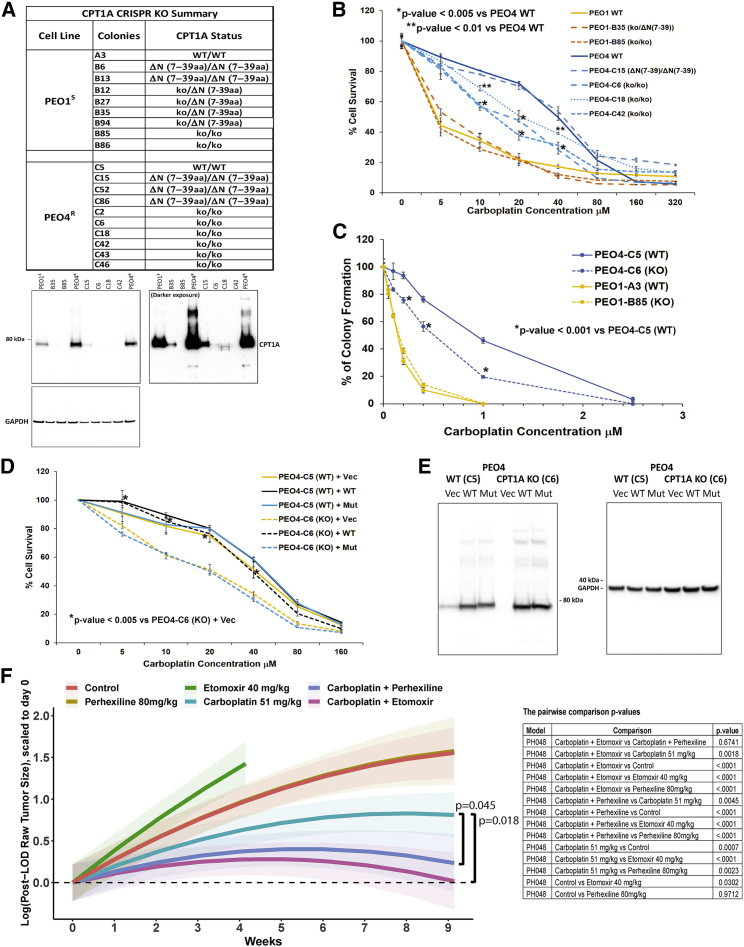
Figure 6.
CPT1A is a determinant of platinum resistance both in vitro and in vivo
(A) Inventory of CPT1A knockout (KO) clones with western blot confirmation in selected clones.
(B) Sensitivity of CPT1A KO clones to carboplatin (cell viability assay, average of 3 biological repeats each with 3 technical repeats).
(C) Sensitivity of selected CPT1A KO clones to carboplatin (colony formation assay). One PEO4 KO clone (C6) and one PEO1 KO clone (B85) were tested along with WT controls (C5 and A3, respectively).
(D) Retroviral complementation of PEO4 CPT1A-KO clone C6 and WT control clone C5. Vec, vector control; WT, WT CPT1A; Mut, mutant CPT1A (G710E) (3 biological repeats each with 3 technical repeats; Student’s t test performed between WT and KO; p values provided in the graph).
(E) Western blot confirmation of the expression of CPT1A WT or G710E mutant in PEO4 cells.
(F) Combination efficacy of carboplatin + CPT1A inhibitors in the platinum refractory HGSOC PDX model PHO48. Tumor area was monitored weekly by transabdominal ultrasound. Change in tumor size over time is plotted as the statistical model estimated average of all animals at each time point for a given treatment, scaled relative to baseline estimate for that treatment. Shading indicates 95% confidence intervals. The p values are provided in the table.