Figure 5.
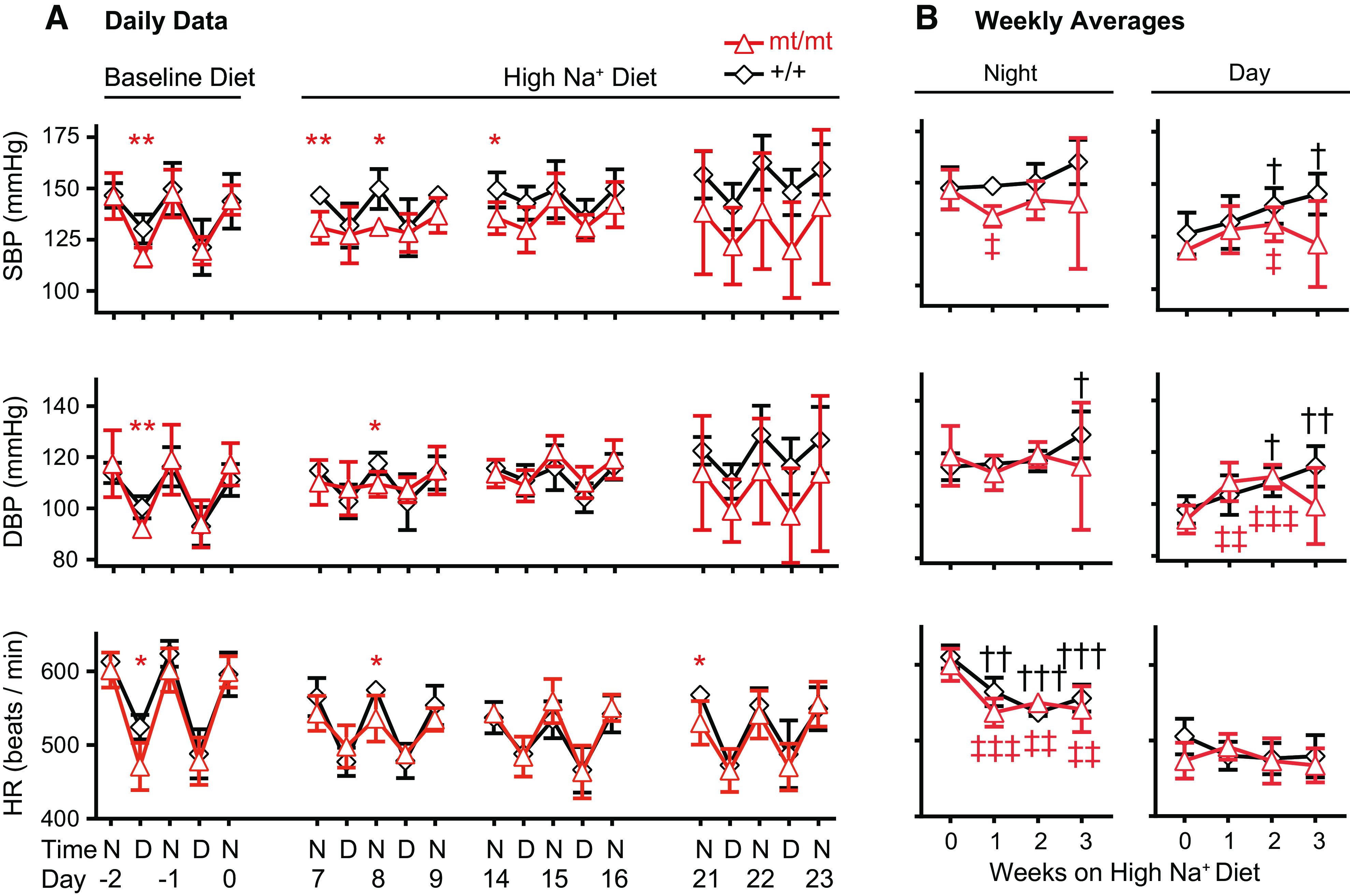
γmt/mt mice exhibit reduced blood pressure (BP) and blunted diurnal BP variation in response to a high-Na+ (4% NaCl) diet (HSD). BPs in 13-wk-old mice were measured via intra-aortic telemetry. A: mean systolic BP (SBP), diastolic BP (DBP), and heart rate (HR) at baseline and after initiation of the HSD. Day 0 represents the day that diets were transitioned from baseline (0.49% NaCl) to the HSD. *P ≤ 0.05 and **P ≤ 0.01 for comparison between genotypic groups on a given day. B: to compare changes in BP or HR against baseline, mean weekly BP or HR, disaggregated into nighttime and daytime measurements, were averaged over the course of the 3 nights and 2 days per week shown in A. Statistically significant differences in BP or HR, compared with baseline (week 0), are indicated by † or ‡ for γ+/+ or γmt/mt animals, respectively. † or P ≤ 0.05; †† or ‡‡P ≤ 0.01; ††† or ‡‡‡P ≤ 0.001. n = 5 mice per group. Significance was evaluated using a two-tailed t test. D, daytime; N, nighttime.
