Figure 2.
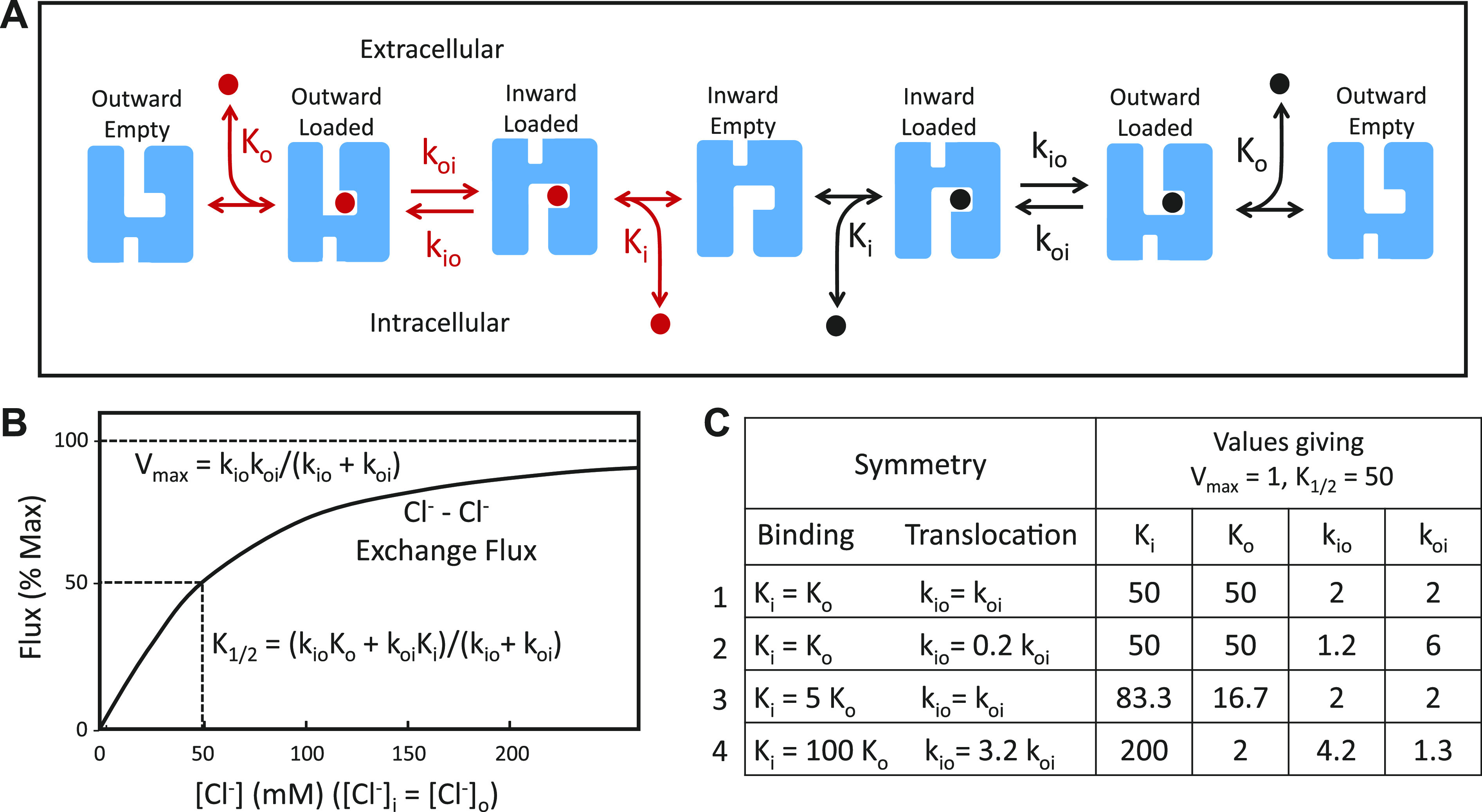
A: catalytic cycle for anion exchange by a ping-pong mechanism. The coupling between influx and efflux results from the extremely slow rate of translocation of the empty transporter. The exchange could be between 2 different ions (red and black), with different dissociation and translocation constants, or it could be tracer exchange of the same anion. B: ping-pong model prediction for the concentration dependence of Cl−/Cl− exchange flux with symmetric Cl− in the absence of competing anions and without any self-inhibition. C: 4 combinations of dissociation constants (Ki, Ko) and translocation rate constants (kio, koi) that all result in the same half-maximal concentration (K1/2) and Vmax for Cl−/Cl− exchange.
