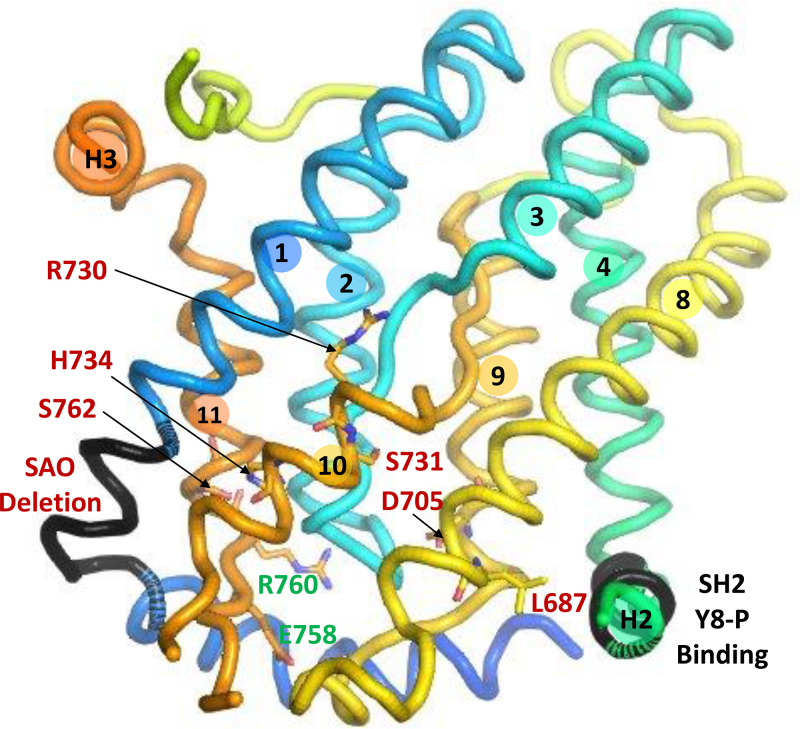
Figure 7.
Band 3 core domain, viewed from the gate/dimerization domain, showing the location of the Southeast Asian ovalocytosis (SAO) deletion (411) and the SH2 sequence that binds cytoplasmic domain phosphorylated at Y8 with transport inhibition (386). Sites of human point mutations that cause increased cation leak and major inhibition of anion transport are labeled in red: L687P, D705Y, S731P, H734R (428), R730C (429, 430), and S762R (431). Mutation G796R (not shown), which also causes cation leak and anion transport inhibition (430, 432), is in the TM12 of the gate domain, facing R730. Two sites (E758K and R760Q) of mutations that cause increased cation leak but do not strongly affect anion exchange are labeled in green.