Figure 6.
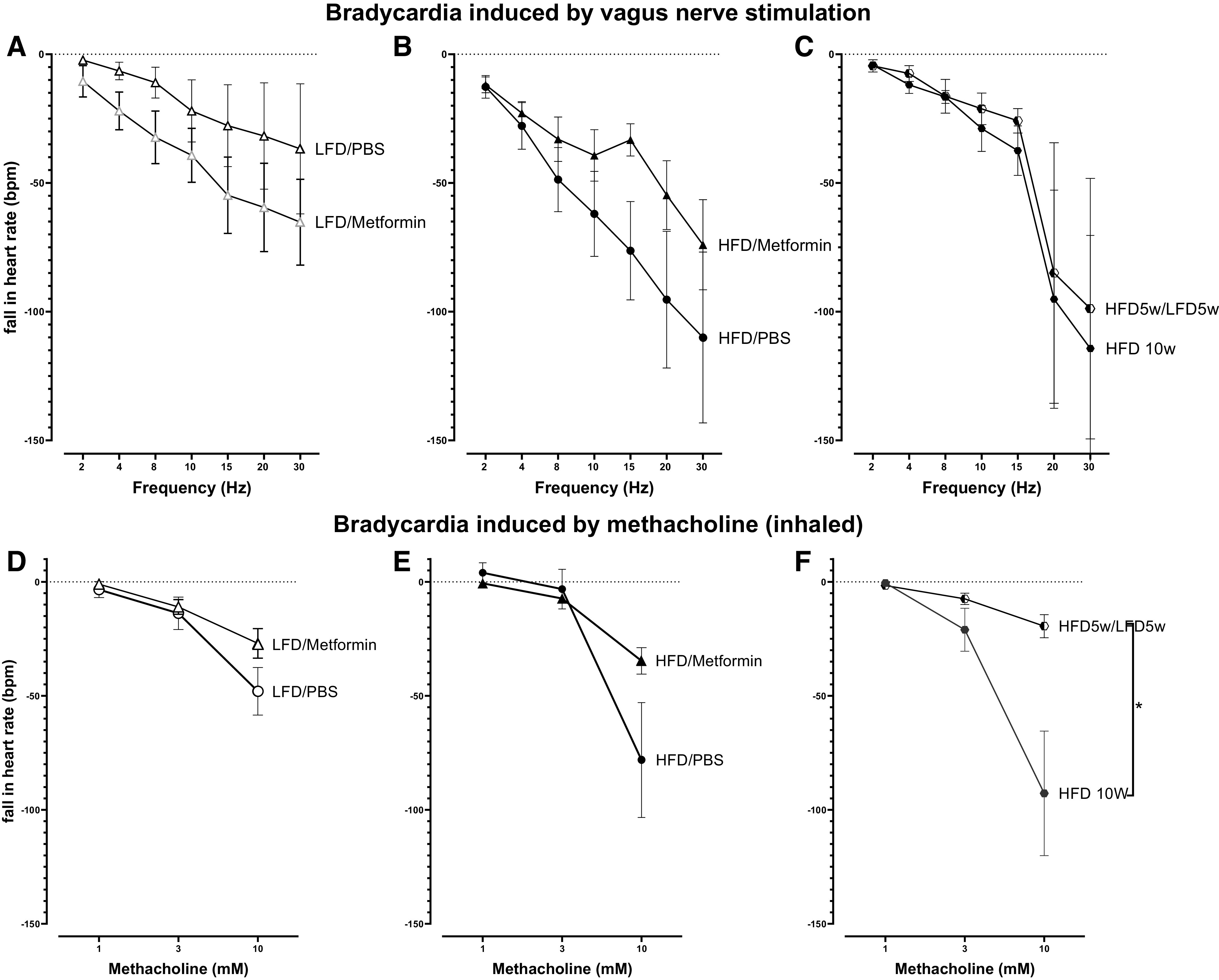
In the heart, vagus nerve electrical stimulation (2–30 Hz) induced bradycardia (measured as a fall in heart rate) that was increased in rats fed a high-fat diet (HFD, B and C) compared with rats fed a low-fat diet (LFD, A), although none of the differences were significant. Bradycardia induced by inhaled methacholine (1–10 mM, delivered in 20 μL of saline) in vagotomized rats was not significantly changed by diet or by metformin (D and E). However, methacholine induced bradycardia was significantly reduced in rats switched from a high-fat diet to a low-fat diet (HFD 5 wk/LFD 5wk) compared with rats on a high-fat diet for 10 wk (HFD 10 wk). n = 6–13. Data are presented as means ± SE. *P < 0.05.
