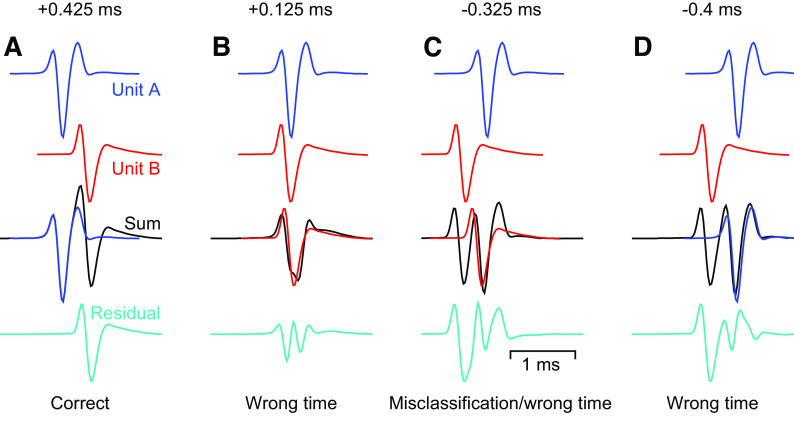
Figure 2.
Greedy template matching systematically fails at certain temporal offsets when spikes from two neurons overlap. Top two rows: average spike waveform templates for two units, unit A (blue) and unit B (red) at slightly different time lags. Third row: a noiseless pseudo voltage trace (black) created by adding the two templates at the temporal offset shown. The binary pursuit algorithm chooses to assign a spike according to the overlaid template. Bottom row: the residual voltage after subtraction of the selected template from the original pseudo-voltage. This is the voltage available to the subsequent iteration of binary pursuit. A–D: examples for 4 separate time lags of a spike from unit B relative to a spike from unit A.