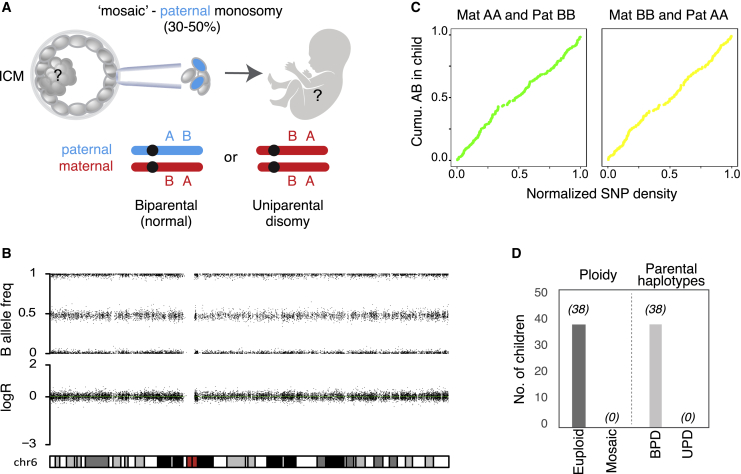
Figure 3.
Euploid biparental inheritance in children born from “mosaic” embryo transfer
(A) Illustration of a mosaic paternal monosomy inferred from the trophectoderm biopsy. The fetal tissues derive from the inner cell mass, which
might contain biparental or uniparental chromosomes or a mixture of them. Supporting SNPs where the maternal and paternal genotypes are homozygous but carry opposite alleles (AA
and BB or vice versa) can be used for determining the presence or absence of parental chromosomes.
(B) LogR and B allele frequencies for chromosome 6 from a child born from group C.
(C) Cumulative AB genotypes in the child of supporting SNPs across chromosome 6.
(D) Number (No.) of children investigated with post
natal SNPa testing. Total number of samples showing euploid or mosaic karyotype (“ploidy”) or containing both parental chromosomes (biparental disomy, BPD) or two homologous chromosomes from the same parent (UPD).