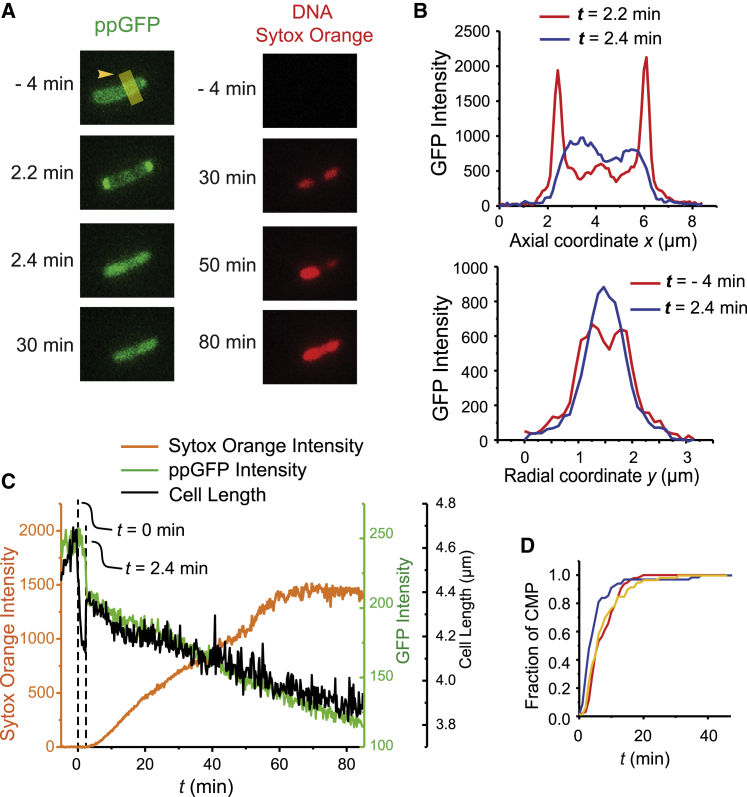
Figure 1.
Effects of copolymer MM-CH on a representative E. coli cell that exports GFP to the periplasm (Video S1). Flow of 2× MIC of MM-CH in EZRDM with 5 nM of the DNA stain Sytox Orange begins at t = 0. Images acquired at 12 s per frame. (A) Fluorescence snapshots of GFP (left) and Sytox Orange (right). (B) Projected axial (top) and transverse (bottom) GFP intensity profiles at the times indicated. (C) Cell length (black), total GFP intensity (green) and Sytox Orange intensity (orange) versus time. Note: scales for GFP intensity and cell length are very different. Over the time interval t = 2–60 min, GFP intensity decreases by 50%, but cell length decreases by only 11%. (D) Cumulative distribution function of the fraction of cells for which CM permeabilization has occurred versus time for LL-37, MM-CH copolymer, and MM homopolymer, each at 2X MIC.