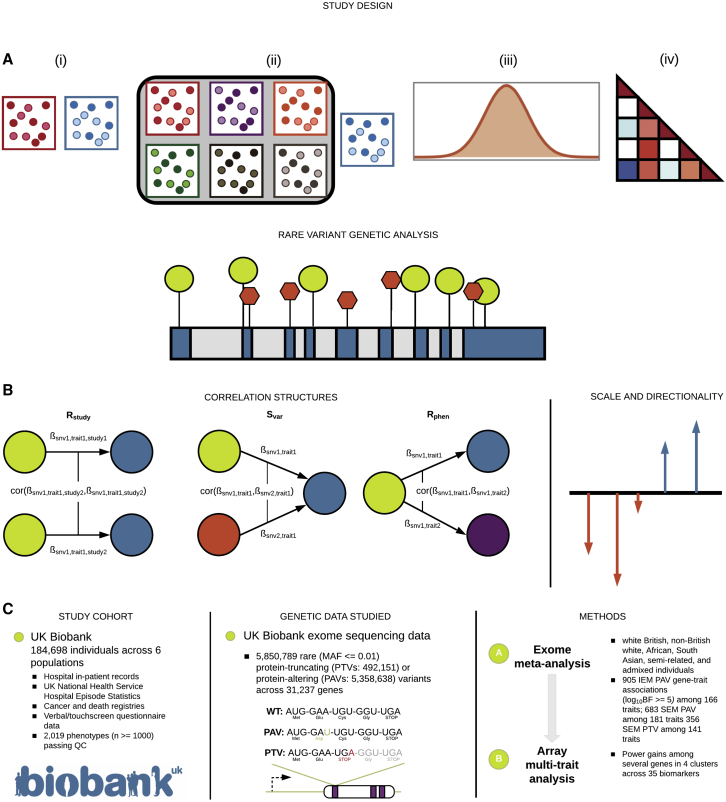
Figure 1.
MRP study overview
(A) MRP is suitable for a broad range of rare variant association study designs, including, from left to right, (i) case-control, (ii) multiple diseases with shared controls, (iii) single quantitative phenotype, and (iv) mixtures of case-control and quantitative phenotypes.
(B) Diagram of factors considered in rare variant association analysis including the correlation matrices: (expected correlation of genetic effects among a group of studies), (expected covariance of genetic effects among a group of variants, potentially accounting for annotation of variants), and (expected correlation of genetic effects among a group of phenotypes). MRP can take into account both scale and direction of effects.
(C) We focused on 184,698 individuals across six ancestry groups in the UK Biobank and analyzed 5,850,789 rare coding variants (492,151 PTVs and 5,358,638 PAVs) in the whole-exome sequencing data via single-trait and multi-trait meta-analyses with a specific focus on 35 biomarker traits.