FIGURE 3.
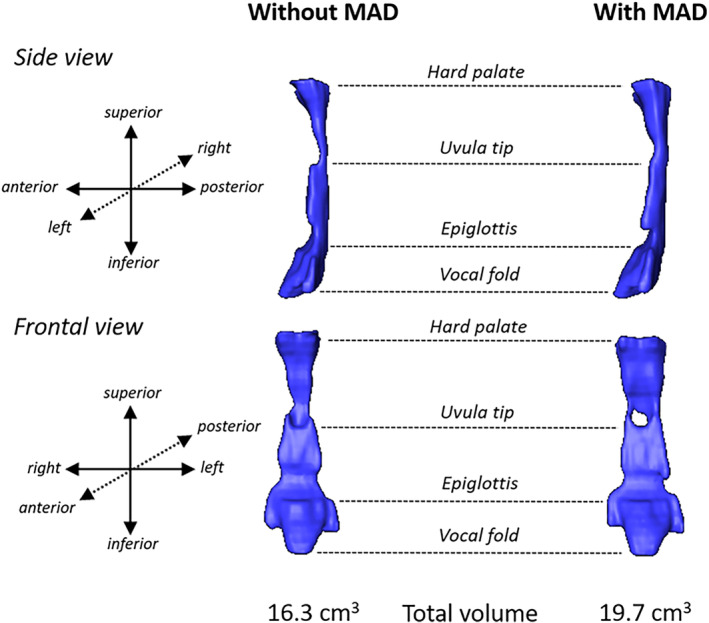
Volumetric reconstructions of the upper airway space constructed from Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans in a MAD treatment responder without and with a MAD in situ. The anatomical landmarks are shown from the hard palate at the top to the vocal folds at the bottom. The reconstructed airway is shown from the side view (sagittal plane) and frontal view (coronal plane). An increase in the airway space can be observed with MAD, particularly in the frontal view where a widening in the coronal plan can be observed at various points along the upper airway. Often this lateral widening is most prominent in the region between the hard palate and uvula tip. The total volume of the airway increased from 16.3 to 19.7 cm3 with MAD. The apnea‐hypopnea index decreased from 42.8 to 10.7 events/h with MAD. MAD, mandibular advancement device
