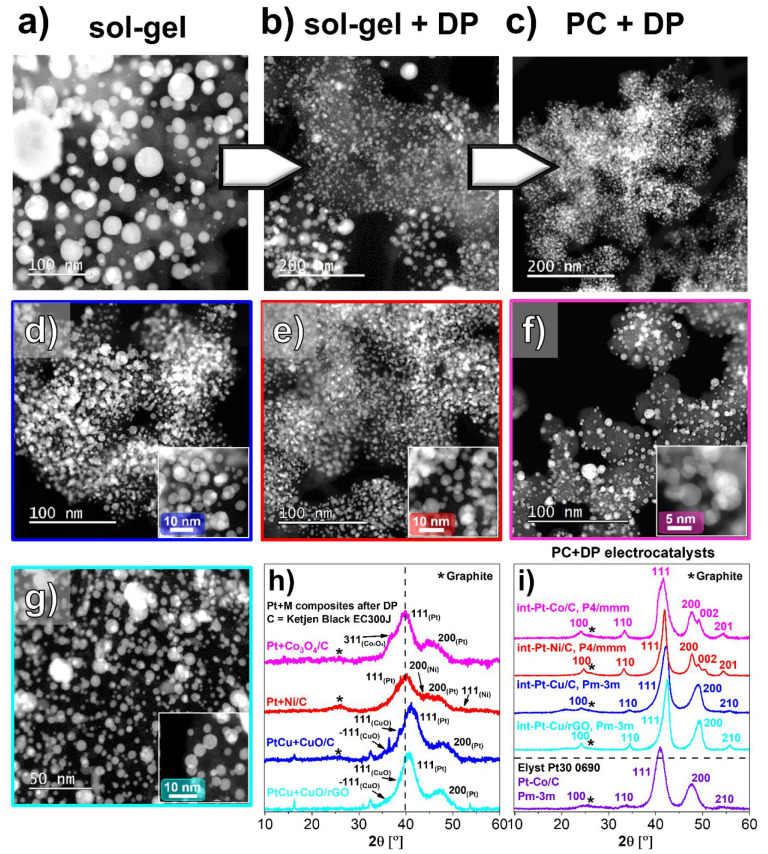
Figure 2.
Improvement in the dispersion of Pt–M NPs over carbon upon transitioning from the (a) sol–gel method for preparation of M/C composites with conventional galvanic displacement for deposition of Pt NPs,43−46 (b) combining sol–gel for preparation of M/C composites with DP method for Pt NP deposition,12,39 and (c) utilizing the synergy between PC methodology for the production of M/C composites in combination with DP method for Pt NP deposition (this work).12,39 (d–g) ADF STEM images of the final d-int-Pt–Cu/C, d-int-Pt–Ni/C, d-int-Pt–Co/C, and d-int-Pt–Cu/rGO electrocatalysts. XRD spectra of (h) Pt + M/C composites (see also Figures S7–S10 for additional STEM characterization), and (i) thermally annealed int-Pt–M/C electrocatalysts (see also Figures S11–S14 for additional STEM characterization). The thermally annealed PC + DP electrocatalysts are compared to a commercial Pt–Co/C reference from Umicore (Elyst Pt30 0690).