Figure 1.
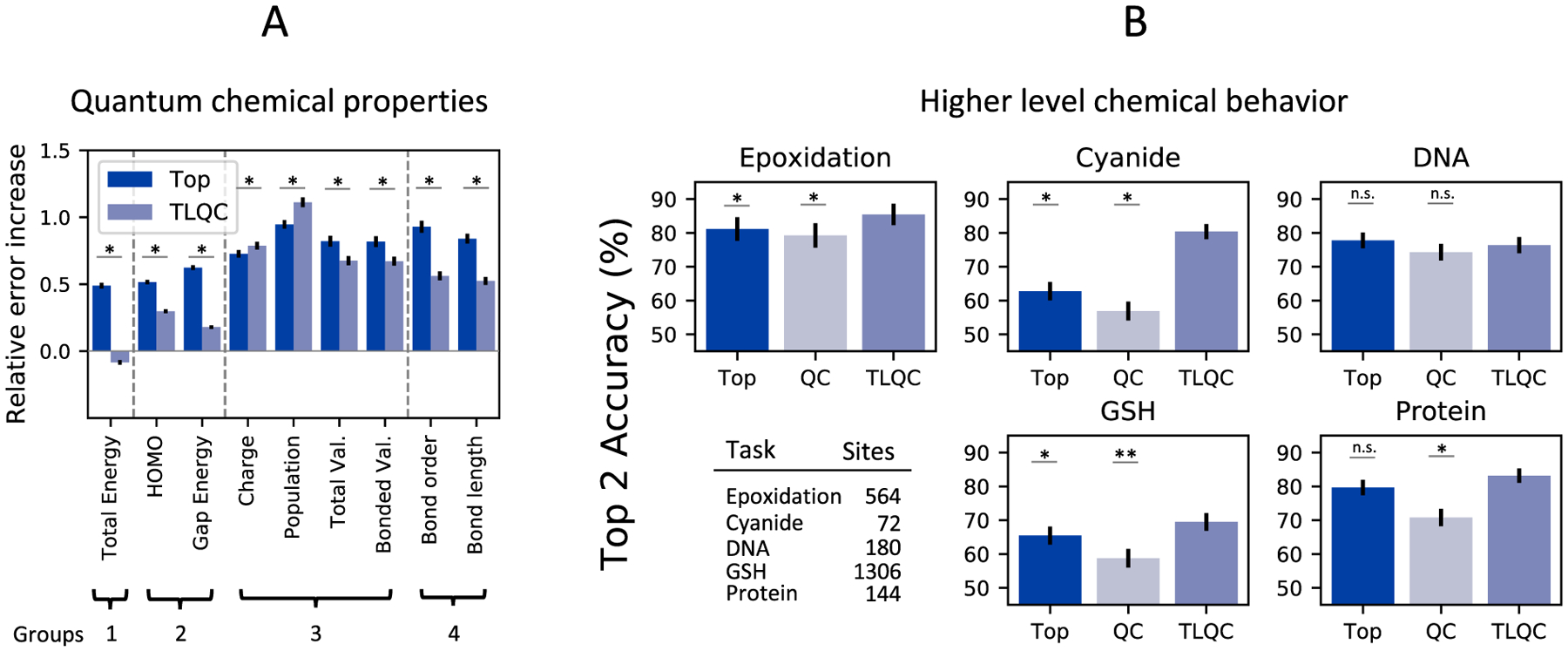
Transfer learning from quantum chemistry can calculate quantum chemical properties and predict higher-level chemical behaviors. (A) Transfer learning using graph representations learned from quantum chemistry (TLQC) can be used to calculate values of unobserved QC properties by training new decoders. TLQC performs better than decoders trained on topology-based graph representations for most QC properties. (B) TLQC predicts the formation of epoxides by P450-mediated metabolism as well as reactivity of small molecules with four important substrates: cyanide, glutathione (GSH), DNA, and protein. This approach improves accuracy on four of the five tasks compared to models using just topological descriptors (TOP) or using quantum chemical descriptors (QC). *p-value <0.05, **p-value <0.001.
