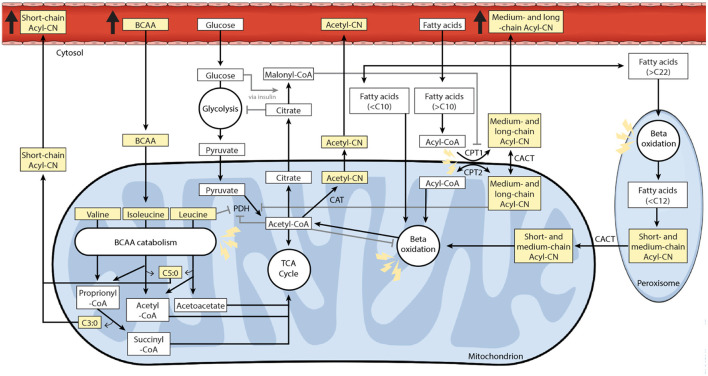
Figure 5.
Acylcarnitine and branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) metabolism in a cardiac cell. This study found elevated levels of circulating short-, medium- and long-chain acylcarnitine and BCAA species in patients with CAD compared to clinically healthy individuals. Under aerobic conditions, lipids represent the main energetic substrate in cardiac cells (33). The main role of carnitine and acylcarnitines is to transport fatty acids, containing acyl-chain(s) of 10 or more carbon atoms, into the mitochondria for subsequent beta-oxidation. The so-called carnitine shuttle includes several enzymes. The enzyme carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1) located at the outer mitochondrial membrane converts acyl-CoAs into acylcarnitines. These are then transported through the inner mitochondrial membrane by the carrier carnitine/acylcarnitine translocase (CACT). Once inside the mitochondrion, the enzyme carnitine palmitoyltransferase 2 (CPT2) converts acylcarnitines back to their corresponding acyl-CoAs, which will then undergo beta-oxidation to produce acetyl-CoA (34–36). Beyond fuel trafficking, acylcarnitines also defend against mitochondrial stress by buffering the intracellular free CoA to acyl-CoA ratio (37–39). The carnitine shuttle enables mitochondrial export of excess carbons in the form of acylcarnitines, which can then be excreted via blood and urine (37, 39). This process also supports metabolic flexibility by relieving the inhibition of PDH induced by acetyl-CoA accumulation (40). Metabolic flexibility is the ability to switch between substrate for energy production depending on substrate availability (41). Fatty acids and glucose intermediates compete as metabolic substrate for energy production in cardiac mitochondria (Randle cycle) (42). Short- and odd-chain acylcarnitine species, such as propionylcarnitine (C3) and isovalerylcarnitine (C5), are usually derived from BCAA catabolism (43–45). Molecules on a yellow background were measured in this study. Regulatory mechanisms are represented with gray lines, normal arrows for stimulation and arrows to bar for inhibition. Lightning icons represent impairment. Acyl-CN, acylcarnitine; BCAA, branched-chain amino acid; C, number of carbon atoms; CACT, carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase; CAT, carnitine acetyltransferase; CPT1, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1; CPT2, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 2; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase.