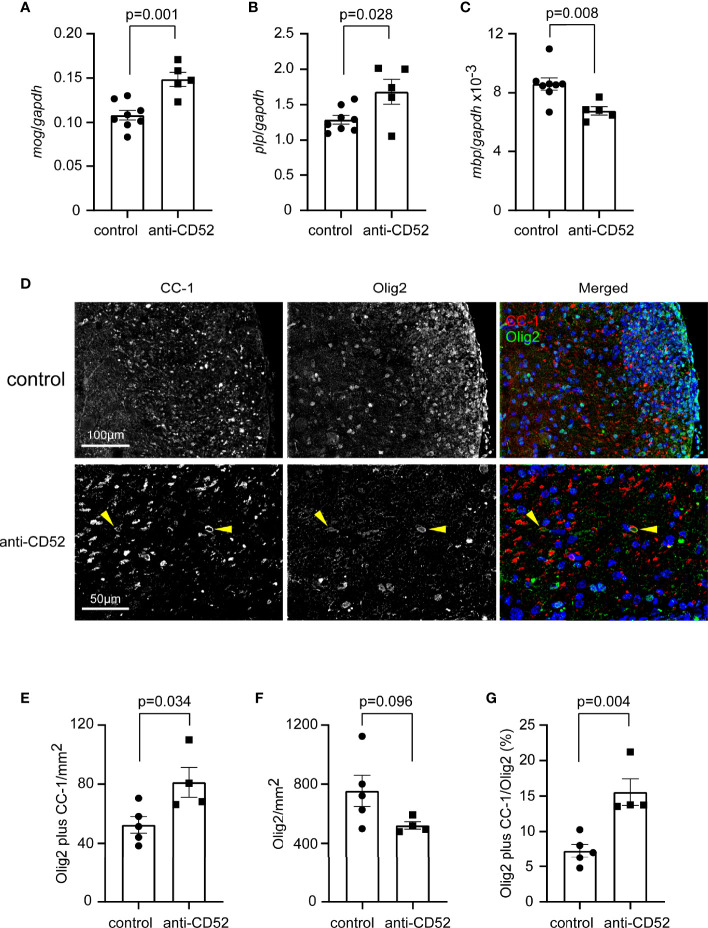
Figure 5.
Treatment with CD52 antibody has a potential to promote remyelination in the spinal cord of C57BL/6J EAE mice. C57BL/6J EAE mice were treated with CD52 antibodies and PBS at the peak of disease. Two weeks later, the spinal cord was isolated for analysis of transcription of myelin protein genes, mog, plp and mbp [(A–C) t test; t (11) = 4.378, 2.526 and 3.208 for mog, plp and mbp, respectively; n ≥ 5 per group] and for the immunohistological analysis of olig2 and CC-1-positive oligodendrocytes. The olig2 and CC-1 double positive oligodendrocytes are indicated with arrow heads (D). Treatments with CD52 antibodies significantly increased the density of olig2/CC-1-positive oligodendrocytes [(E) t test; t (7) = 2.636; n ≥ 4 per group] and tended to decrease the number of single olig2-positive cells [(F) t test; t (7) = 1.926; n ≥ 4 per group]. The percentage of olig2/CC-1-double positive cells among total olig2-positive cells was strongly increased by anti-CD52 therapy [(G) t test; t (7) = 4.252; n ≥ 4 per group].