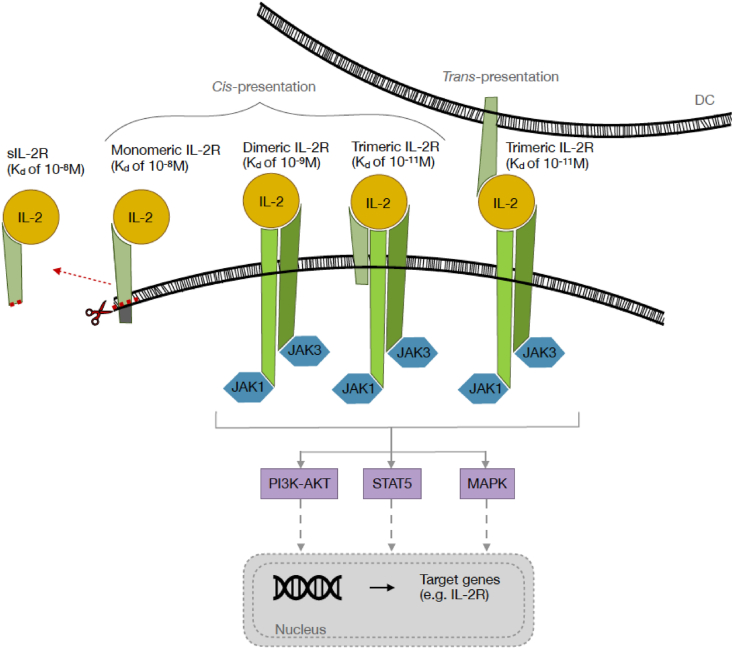
Fig. 1.
The IL-2R classification and the IL-2 – IL-2R signalling pathway. IL-2 binds to the monomeric (low binding affinity: Kd of 10−8 M), dimeric (intermediate binding affinity: Kd of 10−9 M), trimeric (high binding affinity: Kd of 10−11 M) and soluble (binding affinity: Kd of 10−10 M, sIL-2R) IL-2R. The monomeric IL-2R consists of only the IL-2Rα-chain. The heterodimeric receptor is composed of the combination of the IL-2Rβ and -γ forms, while the trimeric receptor combines all three subunits. The trimeric IL-2R can be constructed by the cis-presentation of IL-2Rα on T-cells and the trans-presentation of IL-2Rα on antigen presenting cells (e.g., dendritic cells, DCs). The IL-2Rα-chain can be shed off, generating the sIL-2R. Only the binding of IL-2 to the dimeric and trimeric IL-2Rs results in downstream signalling via three main pathways: PI3K-AKT, STAT5 and MAPK. These pathways activate the transcription of target genes such as the IL2RA gene.