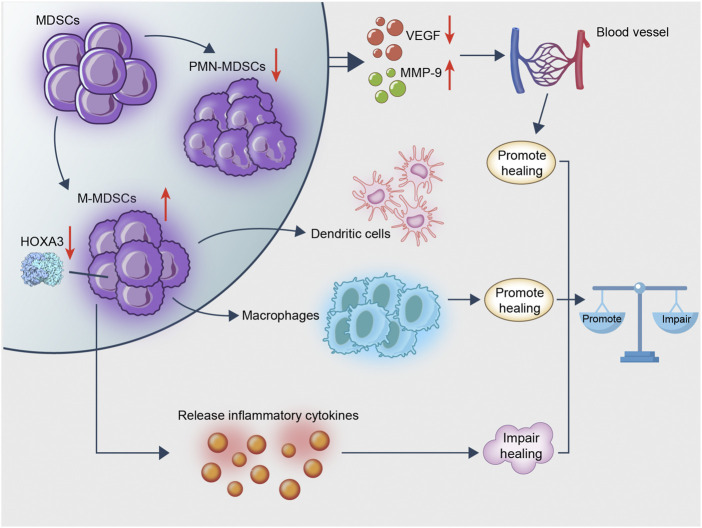
FIGURE 2.
MDSC is rapidly transformed into macrophages following recruitment to the wound. This process exerts an anti-inflammatory effect and promotes wound healing. MDSC remains in diabetic wounds and affects angiogenesis, whereas diabetes hinders the recruitment of MDSC from the wound; the existence of an imbalance ratio of PMN/M-MDSC keeps the wound in an inflammatory microenvironment hindering wound healing. Therefore, MDSC promotes wound healing, whereas excessive M-MDSC impairs wound healing.