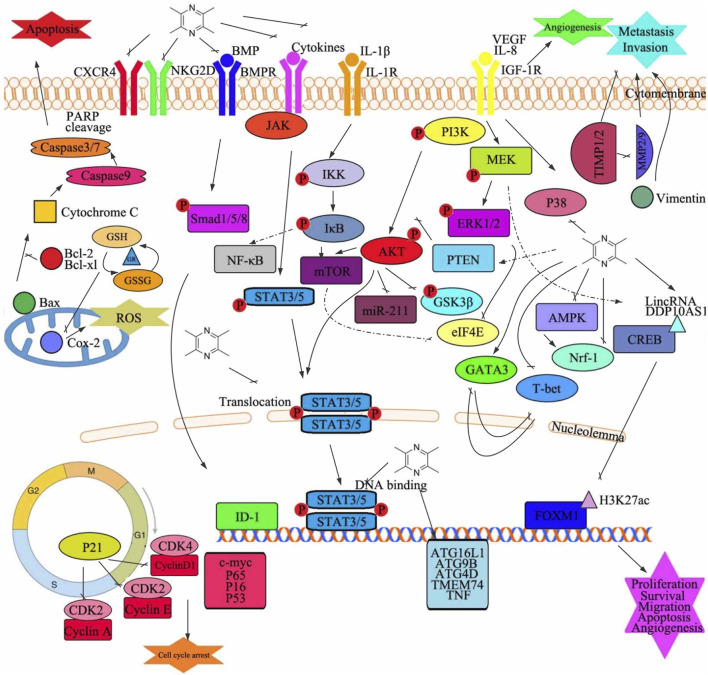
FIGURE 3.
Graphical summary of the antitumor mechanisms underlying the role of tetramethylpyrazine. Tetramethylpyrazine acts on multiple signaling pathways in cancer cells to modulate several changes in phenotype such as cell proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, migration, invasion, and angiogenesis. GSH, glutathione; GR, glutathione reductase; Bax, Bcl2-associated X protein; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; Cox-2, cytochrome c oxidase subunit II; ROS, reactive oxygen species; P, phosphorylation; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; CXCR4, C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4; NKG2D, killer cell lectin-like receptor K1; BMP, bone morphogenetic protein; BMPR, bone morphogenetic protein receptor; JAK, Janus kinase; IL, interleukin; PARP, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; IGF-1R, insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor; IKK, I-kappaB kinase; mTOR, mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase; miR, microRNA; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin; AKT, protein kinase B; GSK3β, glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta; eIF4E, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E; GATA3, GATA-binding protein 3; T-bet, T-box transcription factor 21; Nrf-1, nuclear respiratory factor 1; CREB, DNA-binding transcriptional regulator CreB; AMPK, protein kinase AMP-activated catalytic subunit alpha 1; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; TIMP, tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase; ID-1, inhibitor of DNA binding 1; FOXM1, forkhead box M1; ATG4D, autophagy-related 4D cysteine peptidase; TMEM74, transmembrane protein 74; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; c-myc, transcriptional regulator Myc-like; CDK, cyclin-dependent kinases; ATG16L1, autophagy-related 16 like 1; ATG9B, autophagy-related 9B