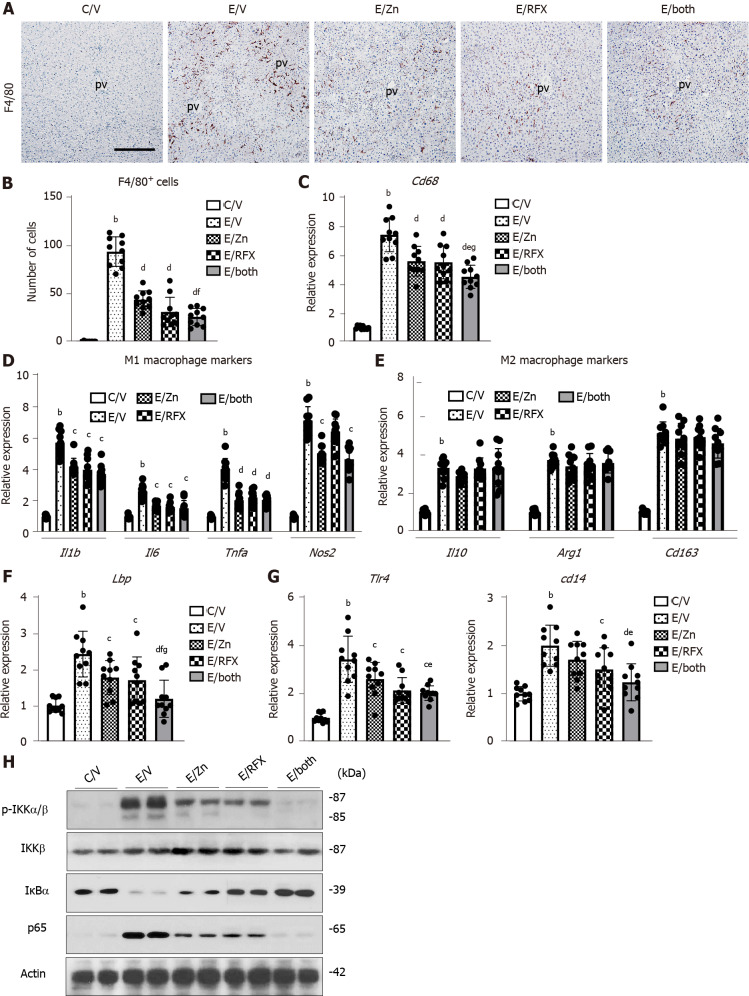
Figure 3.
Zinc acetate and rifaximin against toll-like receptor 4-mediated pro-inflammatory response in alcoholic liver disease mice. A: Representative microphotographs of liver sections stained with F4/80. Scale bar: 50 μm. B: Semi-quantitation of F4/80 immuno-positive Kupffer cells in high-power field by NIH imageJ software. Histochemical quantitative analyses included five fields per section; C-G: Relative mRNA expression level of Cd68 (C), M1-polarized macrophage-related genes (Il1b, Il6, Tnfa and Nos2) (D), M2-polarized macrophage-related genes (Il10, Arg1 and Cd163) (E), Lbp (F), Tlr4 and Cd14 (G) in the liver of experimental mice. The mRNA expression levels were measured by RT-qPCR, and Gapdh was used as internal control. Quantitative values are indicated as fold changes to the values of C/V group; H: Western blots for p-IKKα/β, IKKβ, IkBα and NF-kB p65 in the liver of experimental mice. Actin was used as internal control. Data are mean ± SD (B-G; n = 10), aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs C/V group; cP < 0.05 and dP < 0.01 vs E/V group; eP < 0.05 and fP < 0.01 vs E/Zn group; gP < 0.05 and hP < 0.01 vs E/RFX group. pv: Portal vein.