Fig. 2.
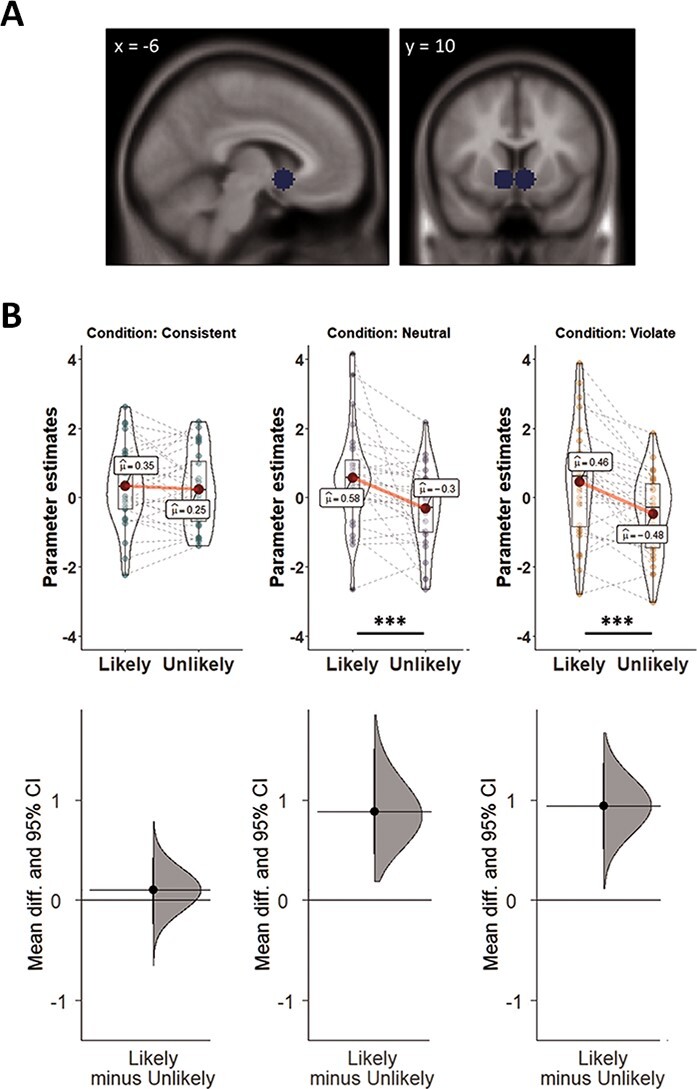
The effect of behavioral ratings of trials on neural responses. In each trial, participants indicated whether they thought the presented target was likely or unlikely to be associated with the presented statement. (A) The independently defined ROIs in the NAcc. (B) We observed a significant interaction in the independently defined NAcc in Study 1: Participants’ ratings modulated the neural response only for stereotype-neutral and stereotype-violating targets, suggesting that stereotype-confirming targets are involuntarily rewarding.
