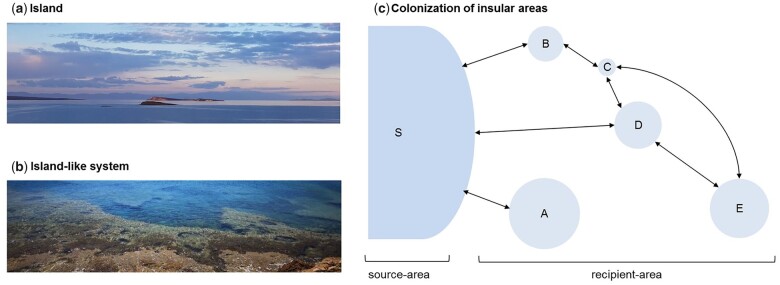
Fig. 1.
(a) Example of a true island (islets close to Lesbos Island, Greece). (b) An island-like system (reef coast in Ano Koufonisi Island, Greece). (c) Colonization of insular areas is the result of migrations between source and recipient areas. Size of recipient areas and distance and connectivity between the site of origin of the migration to recipient area, that is, from the source to recipient area and between recipient areas matter for successful colonization. Here, we present an example of a network between source (S) and recipient areas (A–E). In this network of insular systems, we observe insular areas of different sizes and their potential intraconnections. The size of the circle is proportional to the size of the areas. Arrows show migration can happen back and forth between areas. Photo credit: A. Chroni (2019).