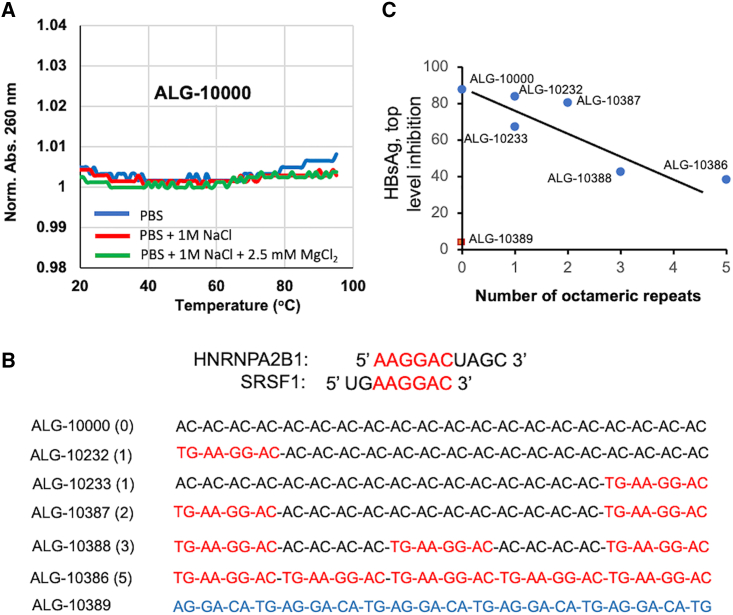
Figure 4.
STOPS interact with multiple host factors to maximally inhibit extracellular HBsAg
(A) ALG-10000 lacks significant intramolecular or intermolecular base-pairing interactions. The absorbance of ALG-10000 under increasing temperature was measured with 2 μM ALG-10000 in three distinct buffers: PBS (blue line), PBS amended with 1 M NaCl (red line), and PBS amended with 1 M NaCl and 2.5 mM MgCl2 (green line). (B) Sequence recognized by host factors HNRNPA2B1 and SRSF1 and built into STOPS molecules. The sequences recognized by both proteins are shown in red. The STOPS molecule's names are followed by parentheses that contain the number of HNRNPA2B1/SFSR1 recognition sequences. The HNRNPA2B1/SRSF1 recognition sequence(s) in the STOPS molecule are shown in red. ALG-10389 is a STOPS molecule that contains five scrambled sequences recognized by HNRNPA2B1 and SRSF1 (blue). (C) The maximum level of HBsAg inhibition decreases with increasing number of the HNRNPA2B1/SFSR1 recognition sequences. ALG-10389 (red square), the STOPS molecule with scrambled nucleotides, was unable to inhibit HBsAg levels.