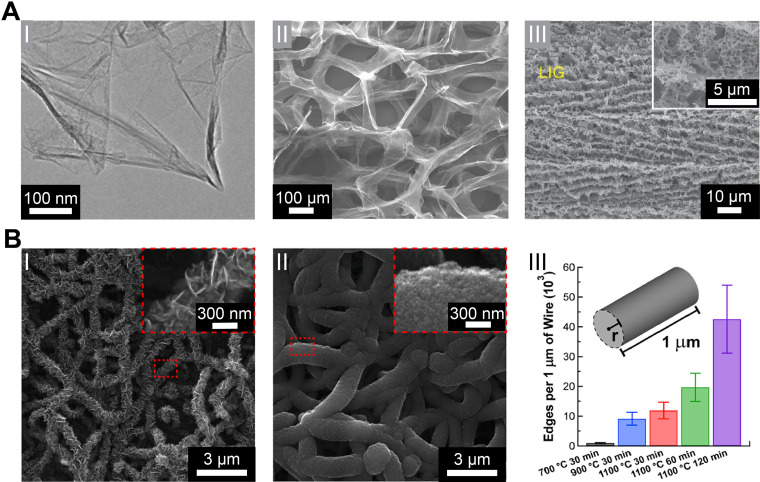
FIG. 3.
Graphene nanostructures. (a) (I) A typical low-magnification transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image of synthesized graphene sheets. Reproduced with permission from Dato et al., Chem. Commun. 40, 6095–6097 (2009). Copyright 2009 The Royal Society of Chemistry.51 (II) Scanning electron micrograph of the microporous graphene foam (GF) structure showing a continuous network of 3D interconnected graphene sheets that comprise the walls of the foam-like structure. Reproduced with permission from Yavari et al., Sci. Rep. 1, 166 (2011). Copyright 2011 Author(s), licensed under a Creative Comments CC-BY-NC-ND License.44 (III) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image of the 3D porous LIG film patterned on polyimide (PI) substrates. Reproduced with permission from Lin et al., Nat. Commun. 5, 5714 (2014). Copyright 2014 Nature Publishing Group.43 (b) Truly 3D topology of graphene. (I–II) Representative SEM images of NT-3DFG synthesized for 30 min at 700 and 1100 °C, respectively. The insets represented by red-dashed boxes show out-of-plane graphene on SiNWs. (III) Number of flake edges along a 1 μm length of the nanowire of radius, r, for all synthesis conditions. Results are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). Reproduced with permission from San Roman et al., ACS Catal. 10(3), 1993–2008 (2020). Copyright 2020 American Chemical Society.49