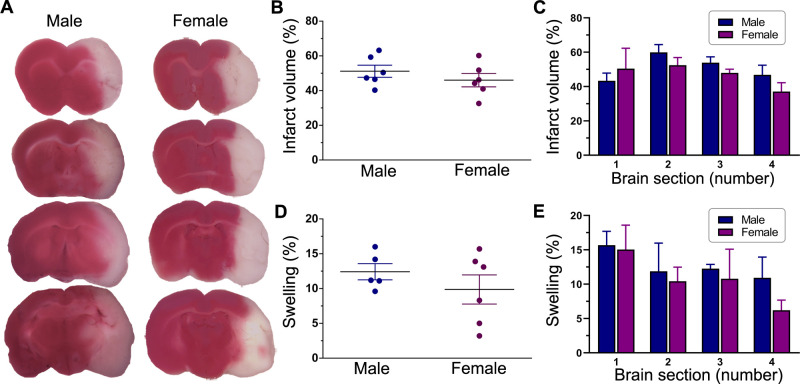
Figure 2.
Post stroke brain damage and swelling. (A) Representative images of TTC-stained serial coronal brain sections from untreated male and female ischaemic rats. Animals were subjected to a 2-hour ischaemia and were subsequently euthanised 1 day after reperfusion. Sections are shown anterior to posterior (top to bottom) and span most of the forebrain from approximately +2 mm to −4 mm from bregma. The red-stained areas indicate normal healthy tissue, whereas the unstained (white) areas ipsilateral to MCAO indicate infarcted tissue. The column scatter plots show the total infarct volume (B) and swelling (D) at 1 day after reperfusion in untreated male and female ischaemic rats. Values are expressed as mean±SEM. Group N’s were six males and six females for infarct volume and five males and six females for swelling. No statistically significant differences were found between the two groups in either infarct volume or brain swelling (p>0.05, unpaired t-test). The bar graphs show the section-by-section analysis of TTC staining in untreated male and female ischaemic rats for infarct volume (C) and swelling (E). Values are expressed as mean+SEM (group N’s as above). Two-way repeated measures analysis of variance did not reveal any significant differences between the two groups in either infarct volume or swelling. MCAO, middle cerebral artery occlusion; TTC, triphenyltetrazolium chloride.