Figure 1. GSK672 treatment decreases hepatic steatosis and injury in the alcohol-fed mice.
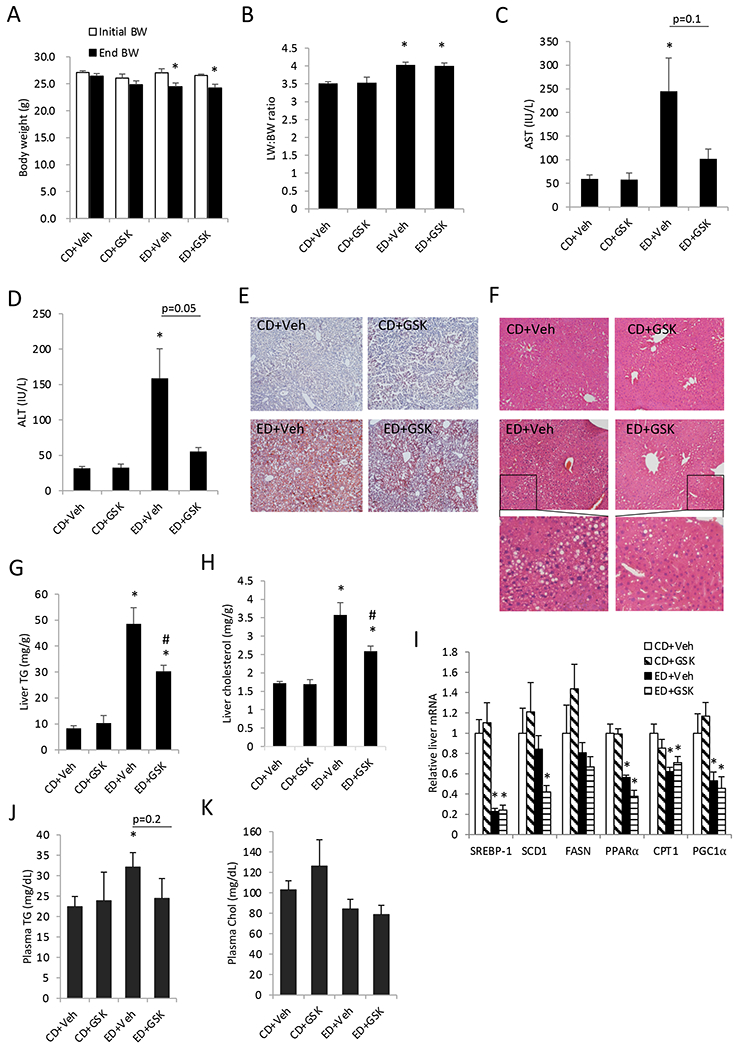
Male C57BL/6J mice were fed control diet (CD) or alcohol diet (ED) and treated with vehicle (Veh) or GSK672 (4 mg/kg/day) as described in the “Materials and Methods”. A. Body weight before and after alcohol feeding. B. Liver weight (LW): body weight (BW) ratio. C. serum AST concentration. D. Serum ALT concentration. E. Representative liver Oil Red O staining. F. Representative liver H&E staining. G. Liver triglyceride (TG) content. H. Liver total cholesterol content. I. Liver mRNA expression. J. Plasma TG concentration. K. Plasma total cholesterol concentration. All results are expressed as mean±SEM (n=5-6). “*”, vs. CD+Veh. “#”, vs. ED+Veh.
