Fig. 2|. Arp2 and Arp3 flatten and adopt the short pitch helical conformation upon activation.
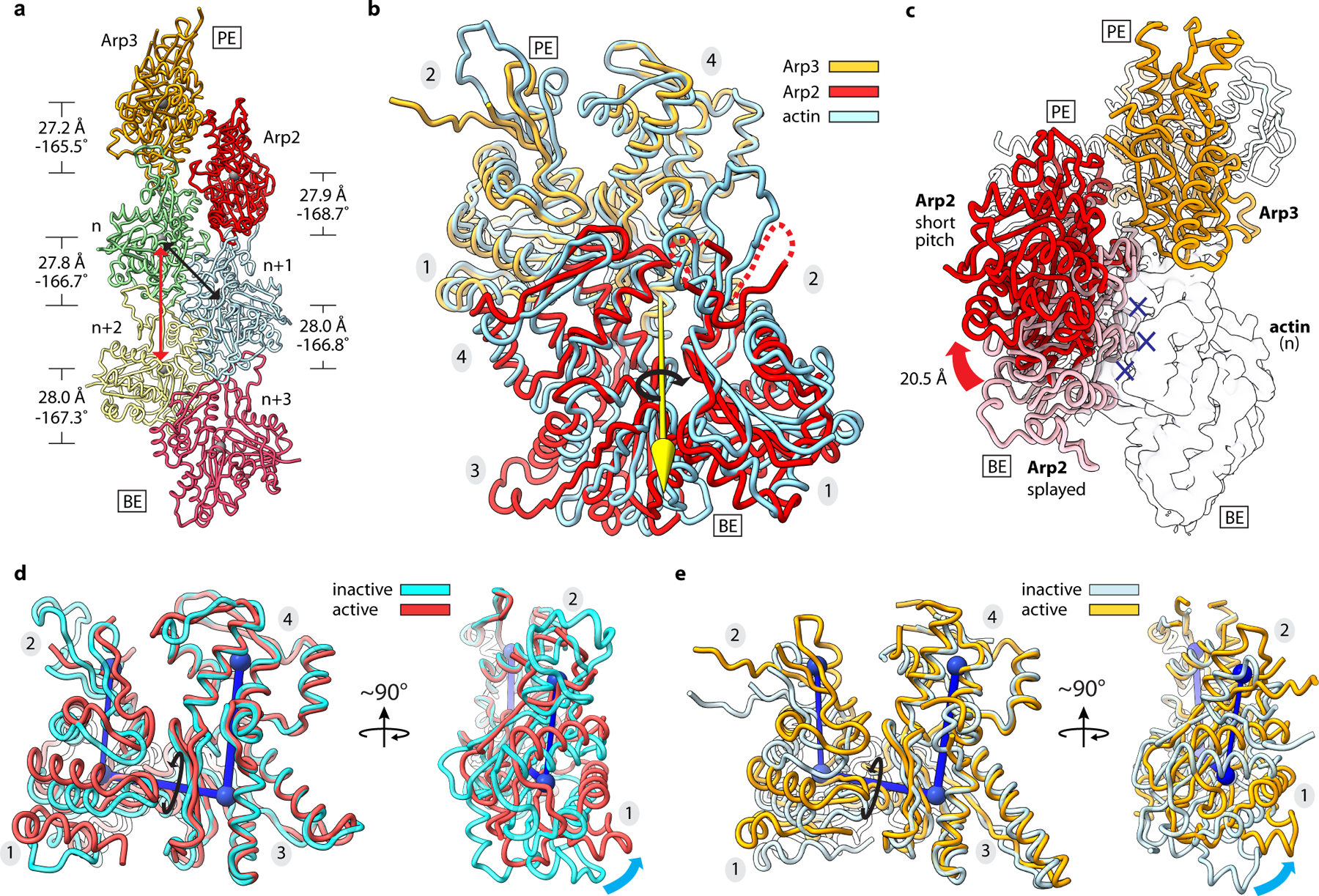
a, Ribbon diagram showing the two actin-related subunits at the pointed end of the nucleated actin-filament. The rise and twist of each subunit is indicated. Black and red arrows show short and long pitch helical interactions within the filament, respectively. b, Superposition of Arp2 and Arp3 from the active structure with a short pitch actin dimer from an actin filament (PDB 6DJO)16. Axis of rotation (yellow arrow) of Arp2 (9°) compared to its equivalent actin subunit in the dimer is shown. Subdomain numbers are shown in grey ovals throughout. c, Movement of Arp2 from the splayed (inactive) to short pitch conformation. Blue X’s show potential steric clash between Arp2 in the splayed conformation and the first actin subunit in the nucleated filament (transparent surface). d, Superposition of Arp2 in the active structure with subdomains 3 and 4 from the inactive structure. Cyan arrows show flattening motion. e, Superposition of Arp3 in the active structure with subdomains 3 and 4 from the inactive structure. PE: pointed end, BE: barbed end.
