Fig. 4|. Nucleotide binding states of the Arps and actin.
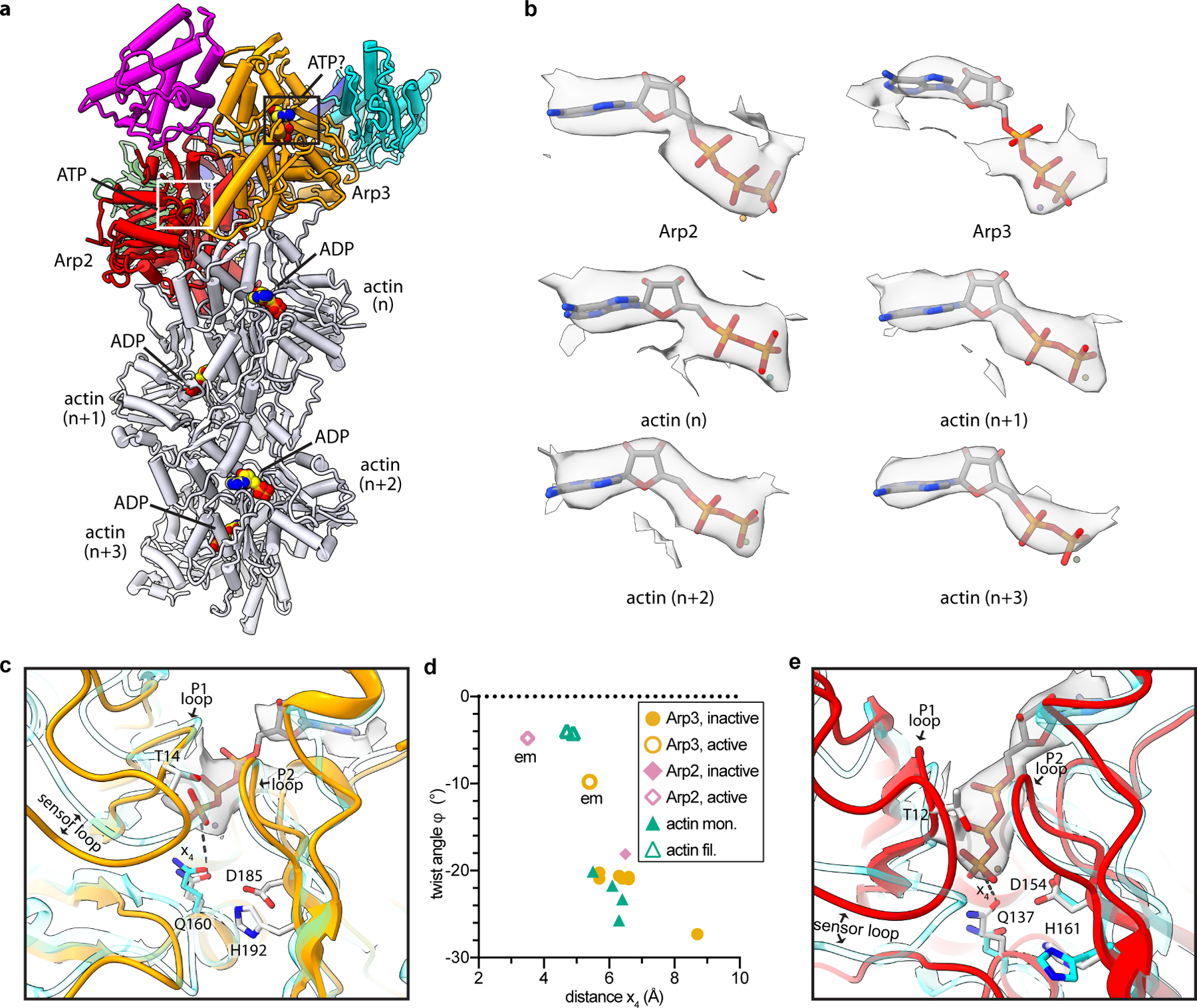
a, Structure of activated Arp2/3 complex with nucleated actin filament in which the bound nucleotides modeled into the Arps and actin subunits are shown as spheres with yellow carbon atoms. b, Individual maps of bound nucleotides (shown in gray) with the corresponding nucleotide structures inside the map. c, Close up of boxed region in panel a showing activated Arp3 (orange) superposed with an AMP-PNP-bound actin subunit from an actin filament PDB 6DJM16 (semi-transparent cyan) using subdomains 3 and 4. Distance x4 between the catalytic glutamine (Q160) and the gamma phosphate is shown as a dotted line. d, Plot of distance x4 for inactive or active Arp2 or Arp3 or monomeric or filamentous structures of actin. All structures had bound ATP or AMP-PNP. Data points labeled “em” are from the activated structure presented here. (See Online Methods for more details) e, Close up of white boxed region in panel a showing activated Arp2 (red) superposed onto inactive Arp2 from the structure PDB 4JD219 (cyan) using subdomains 3 and 4. Flattening rotates Q137Arp2 into or near its presumed catalytically active position.
