Fig. 1: Screening for a K29-linked ubiquitin chain-specific binder and the crystal structure of sAB-K29 in complex with K29-linked diubiquitin.
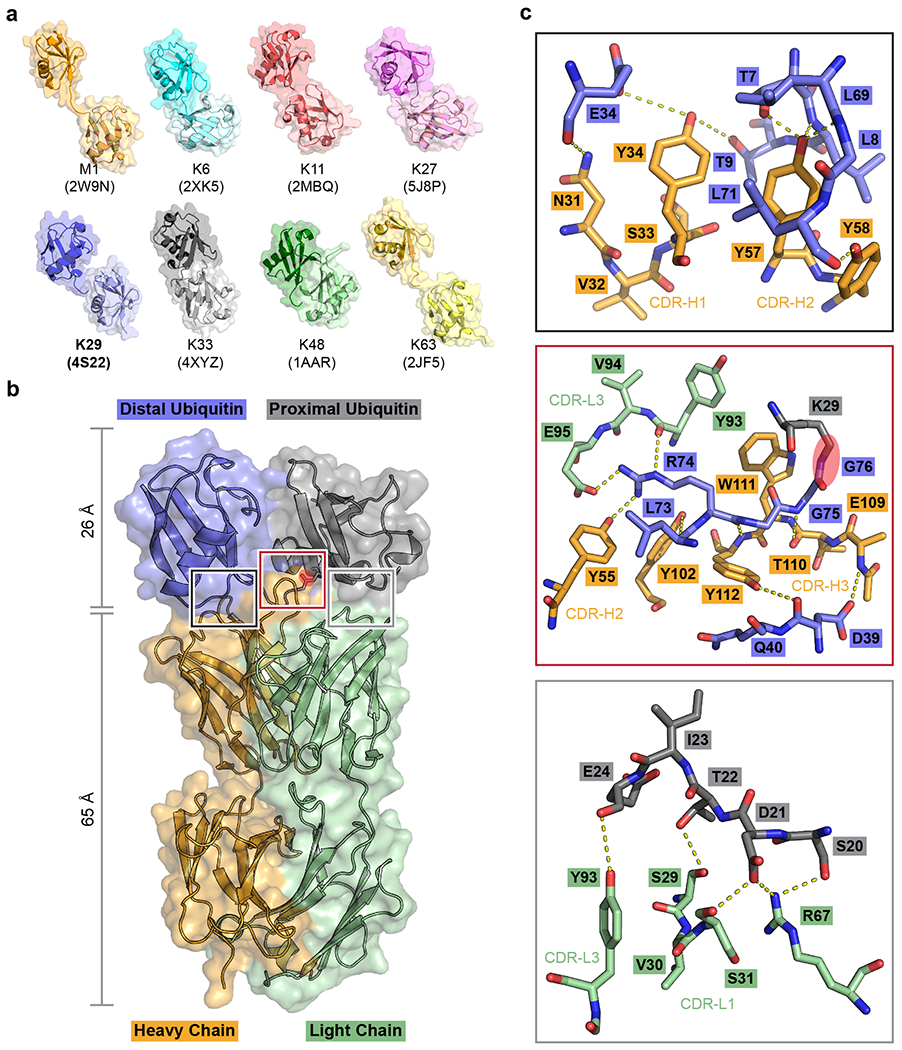
a, Crystal structures of diubiquitin molecules with eight possible linkages. The K29-linked ubiquitin chain was the focus of this study. b, Crystal structure of sAB-K29 in complex with K29-linked diubiquitin determined at a 2.9 Å resolution (Supplementary Table 1). Color code: orange, heavy chain of sAB-K29; green, light chain of sAB-K29; blue, distal ubiquitin; gray, proximal ubiquitin. The isopeptide bond between the C-terminus of the distal ubiquitin molecule and K29 of the proximal ubiquitin molecule is highlighted with a red oval. c, Zoomed-in views of the three binding interfaces between sAB-K29 and the diubiquitin. Top, binding interface between the heavy chain of sAB-K29 and the distal ubiquitin molecule; middle, binding interface between both the heavy and light chains of sAB-K29 and the linker region of the diubiquitin molecule; bottom, binding interface between the light chain of sAB-K29 and the proximal ubiquitin molecule. Potential hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted lines. The isopeptide bond in the middle panel is highlighted with a red oval.
