Extended Data Figure 2:
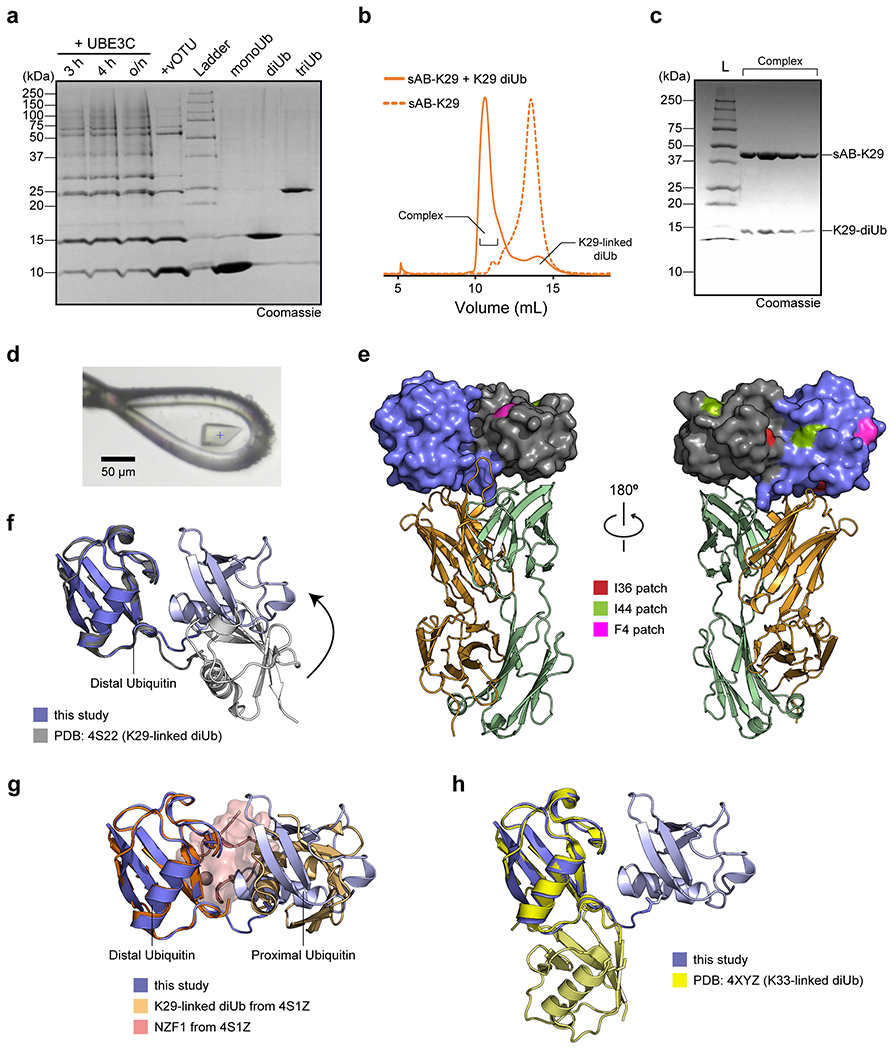
The gel in panel a is a single-time experiment; The gel in panel c are representative of two independent experiments; n = 2. a, Purification of K29-linked diubiquitin. A mixture of K29- and K48-linked polyubiquitin mixture was assembled by incubating monoubiquitin, UBE1, UBE2L3, and UBE3C overnight. vOTU, a DUB that does not cleave K29-linked chains, was added to the reaction mixture to cleave K48-linked polyubiquitin chains. The resulting mono-, di-, and triubiquitin molecules were separated by cation exchange chromatography. b, Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) of sAB-K29 and sAB-K29 in complex with K29-linked diubiquitin. c, The SDS-PAGE gel of the complex peak in panel b. d, A picture of the crystal of the complex mounted in a cryo-loop. e, The distribution of hydrophobic patches on K29-linked diUb. Only the I36 patch of the distal ubiquitin molecule is involved in the interaction with the heavy chain of sAB-K29. The colour code of the complex is the same as that in Fig. 1b. f, Superimposition of the crystal structure of K29-linked diUb (PDB accession code: 4S22) and K29-linked diUb in the complex structure determined in this study. The distal ubiquitin molecules in the two structures were aligned. g, Superimposition of the crystal structure of K29-linked diUb in complex with NZF1 domain of TRABID (PDB accession code: 4S1Z) and K29-linked diUb in the complex structure determined in this study. The distal ubiquitin molecules in the two structures were aligned. NZF1 domain was coloured in pink. h, Superimposition of the crystal structure of K33-linked diUb (PDB accession code: 4XYZ) and K29-linked diUb in the complex structure determined in this study. The distal ubiquitin molecules in the two structures were aligned. The K29-linked diUb from this study in panels f-h are in the same orientation as in Fig. 1b and left of panel e.
